Exam Details
Exam Code
:NSE4_FGT-7.2Exam Name
:Fortinet NSE 4 - FortiOS 7.2Certification
:Fortinet CertificationsVendor
:FortinetTotal Questions
:185 Q&AsLast Updated
:Aug 11, 2025
Fortinet Fortinet Certifications NSE4_FGT-7.2 Questions & Answers
-
Question 121:
What are two functions of the ZTNA rule? (Choose two.)
A. It redirects the client request to the access proxy.
B. It applies security profiles to protect traffic.
C. It defines the access proxy.
D. It enforces access control.
-
Question 122:
Refer to the exhibit.
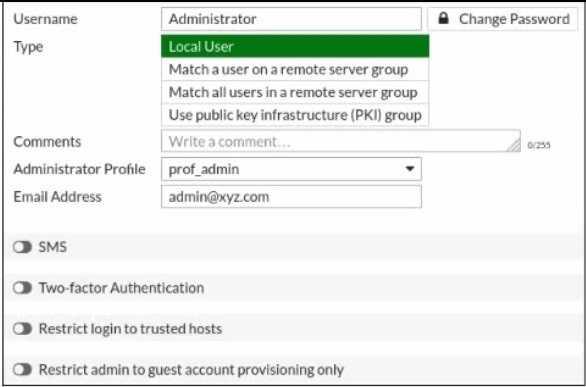
The global settings on a FortiGate device must be changed to align with company security policies. What does the Administrator account need to access the FortiGate global settings?
A. Change password
B. Enable restrict access to trusted hosts
C. Change Administrator profile
D. Enable two-factor authentication
-
Question 123:
Refer to the exhibit.
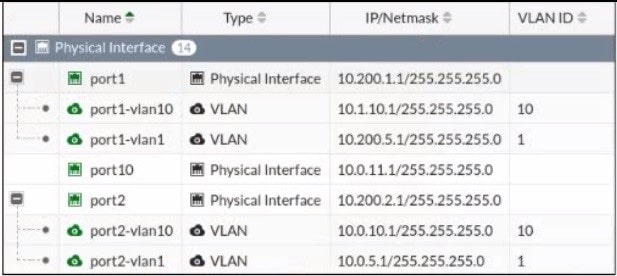
Given the interfaces shown in the exhibit. which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
A. Traffic between port2 and port2-vlan1 is allowed by default.
B. port1-vlan10 and port2-vlan10 are part of the same broadcast domain.
C. port1 is a native VLAN.
D. port1-vlan and port2-vlan1 can be assigned in the same VDOM or to different VDOMs.
-
Question 124:
Refer to the exhibit, which contains a static route configuration. An administrator created a static route for Amazon Web Services.
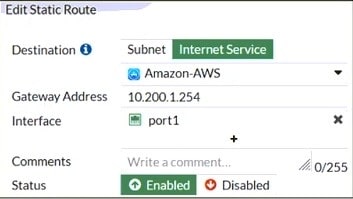
Which CLI command must the administrator use to view the route?
A. get router info routing-table database
B. diagnose firewall route list
C. get internet-service route list
D. get router info routing-table all
-
Question 125:
Refer to the exhibit.
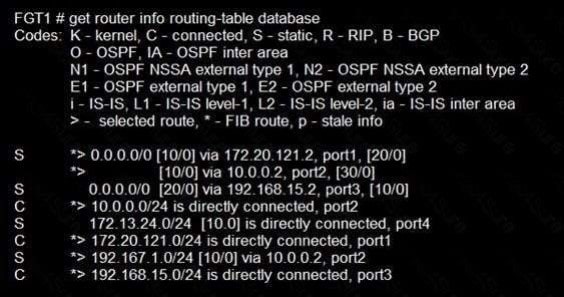
Given the routing database shown in the exhibit, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
A. The port3 default route has the lowest metric.
B. The port1 and port2 default routes are active in the routing table.
C. The ports default route has the highest distance.
D. There will be eight routes active in the routing table.
-
Question 126:
Which two protocols are used to enable administrator access of a FortiGate device? (Choose two.)
A. SSH
B. HTTPS
C. FTM
D. FortiTelemetry
-
Question 127:
Refer to the exhibit.
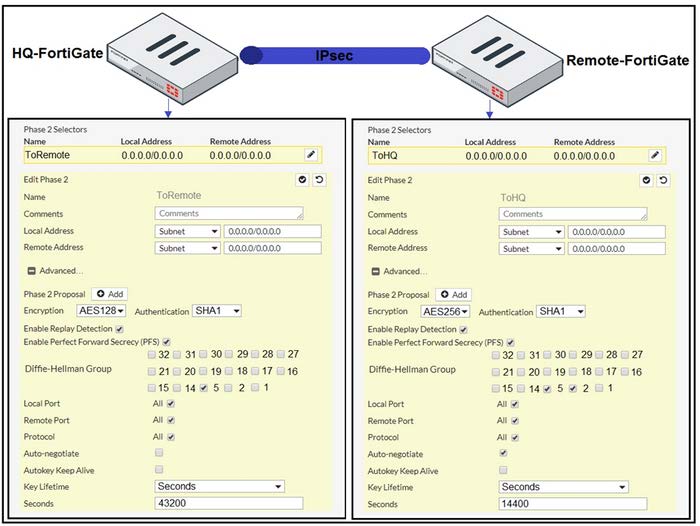
A network administrator is troubleshooting an IPsec tunnel between two FortiGate devices. The administrator has determined that phase 1 status is up. but phase 2 fails to come up. Based on the phase 2 configuration shown in the exhibit, what configuration change will bring phase 2 up?
A. On HQ-FortiGate, enable Auto-negotiate.
B. On Remote-FortiGate, set Seconds to 43200.
C. On HQ-FortiGate, enable Diffie-Hellman Group 2.
D. On HQ-FortiGate, set Encryption to AES256.
-
Question 128:
An administrator is configuring an Ipsec between site A and siteB. The Remotes Gateway setting in both sites has been configured as Static IP Address. For site A, the local quick mode selector is 192. 16. 1.0/24 and the remote quick mode selector is 192. 16.2.0/24. How must the administrator configure the local quick mode selector for site B?
A. 192. 168.3.0/24
B. 192. 168.2.0/24
C. 192. 168. 1.0/24
D. 192. 168.0.0/8
-
Question 129:
Refer to the exhibits.
The exhibits show a network diagram and firewall configurations.
An administrator created a Deny policy with default settings to deny Webserver access for Remote-User2. Remote-User1 must be able to access the Webserver. Remote-User2 must not be able to access the Webserver.
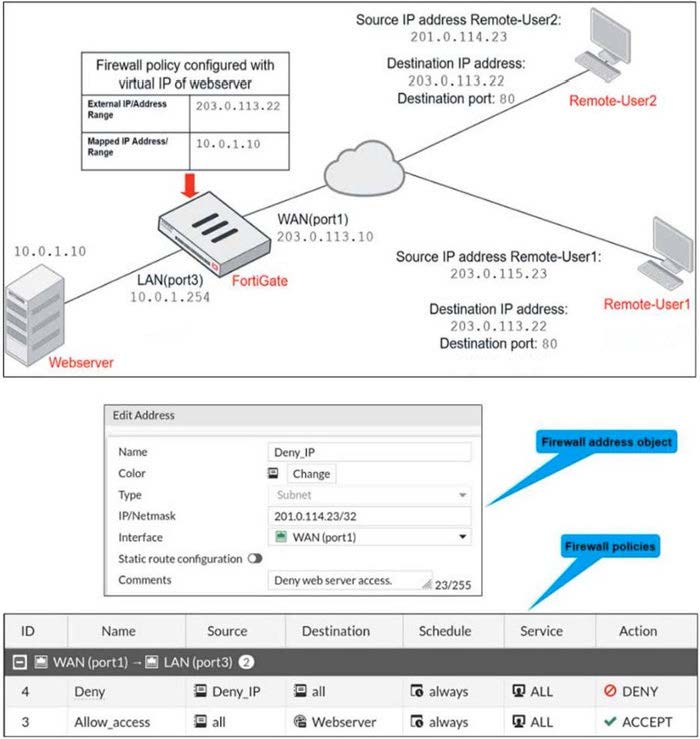
In this scenario, which two changes can the administrator make to deny Webserver access for Remote-User2? (Choose two.)
A. Disable match-vip in the Deny policy.
B. Set the Destination address as Deny_IP in the Allow-access policy.
C. Enable match vip in the Deny policy.
D. Set the Destination address as Web_server in the Deny policy.
-
Question 130:
Which two statements explain antivirus scanning modes? (Choose two.)
A. In proxy-based inspection mode, files bigger than the buffer size are scanned.
B. In flow-based inspection mode, FortiGate buffers the file, but also simultaneously transmits it to the client.
C. In proxy-based inspection mode, antivirus scanning buffers the whole file for scanning, before sending it to the client.
D. In flow-based inspection mode, files bigger than the buffer size are scanned.
Related Exams:
FCP_FAZ_AD-7.4
FCP - FortiAnalyzer 7.4 AdministratorFCP_FGT_AD-7.4
FCP - FortiGate 7.4 AdministratorFCP_FGT_AD-7.6
FortiGate 7.6 Administrator FCP_FGT_AD-7.6FCP_WCS_AD-7.4
FCP - AWS Cloud Security 7.4 AdministratorFCSS_EFW_AD-7.4
FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.4 AdministratorFCSS_NST_SE-7.4
FCSS - Network Security 7.4 Support EngineerFCSS_SASE_AD-24
FCSS - FortiSASE 24 AdministratorNSE4_FGT-5.6
Fortinet NSE 4 - FortiOS 5.6NSE4_FGT-6.0
Fortinet NSE 4 - FortiOS 6.0NSE4_FGT-6.4
Fortinet NSE 4 - FortiOS 6.4
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Fortinet exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your NSE4_FGT-7.2 exam preparations and Fortinet certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.