Exam Details
Exam Code
:IMANET-CMAExam Name
:Certified Management Accountant (CMA)Certification
:IMANET CertificationsVendor
:IMANETTotal Questions
:1336 Q&AsLast Updated
:Jul 11, 2025
IMANET IMANET Certifications IMANET-CMA Questions & Answers
-
Question 121:
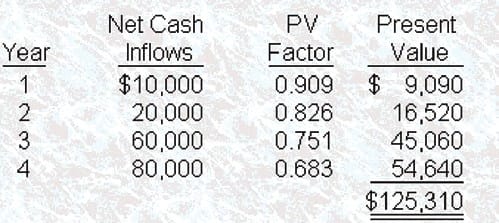
Benet, Inc. uses the net present value method to evaluate capital projects. Bonnet's required rate of return is 10%. Benet is considering two mutually exclusive projects for its manufacturing business. Both projects require an initial outlay of $120,000 and are expected to have a useful life of four years. The projected after-tax cash flows associated with these projects are as follows:
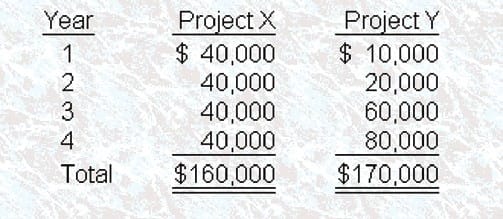
Assuming adequate funds are available, which of the following project options would you recommend that Bennet's management undertake?
A. Project X only.
B. Project Y only.
C. Projects X and Y.
D. Neither project.
-
Question 122:
Gibber Corporation has an opportunity' to sell newly developed product in the United States for a period of five years. The product license would be purchased from New Group Company. Gibber would be responsible for all distribution and product promotion costs. New Group has the option to renew the agreement, with modifications, at the end of the initial five-year term. Gibber has developed the following estimated revenues and costs that would be associated with the new product:

The working capital required to support the new product would be released for investment elsewhere if the product licensing agreement is not renewed. Using the net present value method of analysis and ignoring the effects of income taxes, the net present value of this product agreement, assuming Gibber has a 20% cost of capital, would be
A. $7,720
B. $(64,064)
C. $(72,680)
D. $(127,320)
-
Question 123:
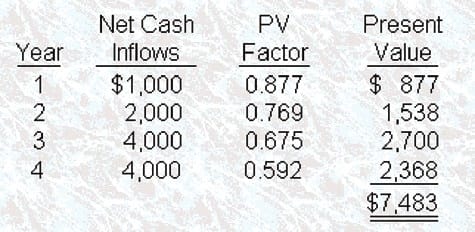
Wilkinson, Inc., which has a cost of capital of 12%, invested in a project with an internal rate of return (IRR) of 14%. The project is expected to have a useful life of four years, and it will produce net cash inflows as follows:
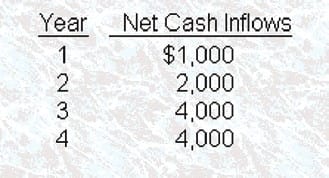
The initial cost of this project amounted to
A. $7,483
B. $9,647
C. $11,000
D. $12,540
-
Question 124:
Assume that the interest rate is greater than zero. Which of the following cash-inflow streams should you prefer?
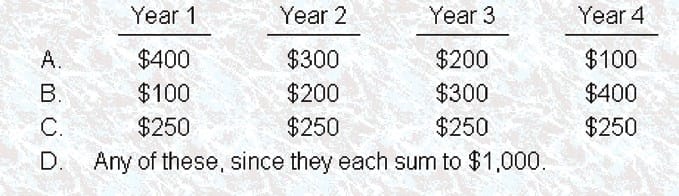
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 125:
The present value may be calculated for discounted cash Inflows Outflows Annuities
A. Yes Yes Yes
B. Yes No Yes
C. No Yes No
D. No No Yes
-
Question 126:
Basic time value of money concepts concern Interest Factors Risk Cost of capital
A. Yes Yes No
B. Yes No Yes
C. No Yes No
D. No No Yes
-
Question 127:
An advantage of the net present value method over the internal rate of return model in discounted cash flow analysis is that the net present value method
A. Computes a desired rate of return for capital projects.
B. Can be used when there is no constant rate of return required for each year of the project.
C. Uses a discount rate that equates the discounted cash inflows with the outflows.
D. Uses discounted cash flows whereas the internal rate of return model does not.
-
Question 128:
In evaluating a capital budget project, the use of the net present value (NPV) model is generally not affected by the
A. Method of funding the project.
B. Initial cost of the project.
C. Amount of added working capital needed for operations during the term of the project.
D. Project's salvage value.
-
Question 129:
All of the following are the rates used in net present value analysis except for the
A. Cost of capital.
B. Hurdle rate.
C. Discount rate.
D. Accounting rate of return.
-
Question 130:
The internal rate of return is
A. The breakeven borrowing rate for the project in question.
B. The yield rate/effective rate of interest quoted on long-term debt and other instruments.
C. Favorable when it exceeds the hurdle rate.
D. All of the answers are correct.
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only IMANET exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your IMANET-CMA exam preparations and IMANET certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.