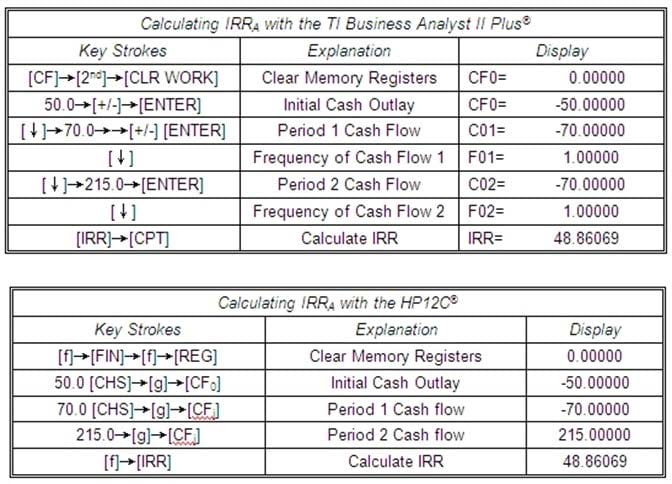
Exam Details
Exam Code
:CFA-LEVEL-1Exam Name
:CFA Level I - Chartered Financial AnalystCertification
:CFA Institute CertificationsVendor
:CFA InstituteTotal Questions
:3960 Q&AsLast Updated
:May 27, 2025
CFA Institute CFA Institute Certifications CFA-LEVEL-1 Questions & Answers
-
Question 1471:
Assume an investor makes the following investments:
During year one, the stock paid a $5.00 per share dividend. In year 2, the stock paid a $7.50 per share
dividend. The investor's required return is 35.0 percent.
The dollar-weighted return is:
A. 48.9%.
B. 16.1%.
C. 46.5%.
D. 102.4%.
-
Question 1472:
Consider the following information for Magical Interactions, Inc.
Based on the assumptions above, which of the following statements is TRUE?
A. The stock is undervalued.
B. If the earnings retention rate increases, the value of the stock will increase (all else equal).
C. If management can increase the EBITDA ratio by only 1.0%, the stock will be properly priced (all else equal).
D. If inflation expectations decrease, the value of the stock will increase (all else equal).
-
Question 1473:
Ted McGovern works in the economics branch of a government bank regulator. When he arrives at work
this morning and checks his voicemail, he has a message from the Regional Director asking him to
calculate the expected rate of return for a stock market series. More detailed information will be
forthcoming in an e-mail. Fortunately, McGovern still has his CFA Program study guides in his office and
finds the correct formulas. McGovern logs on to the computer network and downloads an attachment that
contains the following estimates:
Overall Assumptions:
Index Estimates ?Bull Market:
Index Estimates ?Bear Market:
The expected return on the index is closest to:
A. 67.4%.
B. 39.4%.
C. 30.8%.
D. 98.2%.
-
Question 1474:
Daniel Tipton and Jesse Torrez are first-year MBA students at the Haas School of Business. Torrez has an economics background, but Tipton's background is in music. To help Tipton study one of the main tenets of competition theory, Torrez creates the following question and asks Tipton to identify the statement that is most inconsistent with Porter's five forces. Which statement should Tipton select?
A. Supplier power is higher when there are only a few suppliers to an industry.
B. To sustain above average returns on invested capital, firms should strive for economies of scale.
C. Porter's five forces are: rivalry among current competitors, economies of scale, threat of substitutes, bargaining power of suppliers, and bargaining power of buyers.
D. Rivalry increases when firms of equal size compete within an industry.
-
Question 1475:
Given the following estimated financial results, value the stock of Magic Holdings, Inc. using the infinite period dividend discount model (DDM). Which of the following choices is closest to the value of Magic Holding Inc. stock? (Note: Carry calculations out to at least 3 decimals.)
A. $44.64.
B. $23.54.
C. Unable to calculate stock value because ke < g.
D. $109.27.
-
Question 1476:
Tamira Scott, CFA, manager of an index fund, needs to raise money soon (although not immediately) to pay taxes. Although she believes in the efficient market hypothesis (EMH), she remembers that there are a few anomalies she may take advantage of to earn higher returns. Which of the following actions is most unlikely to provide excess returns? Scott should purchase stocks in:
A. companies with low price/earnings ratios and/or with high book to market ratios.
B. companies that announce stock splits.
C. companies not followed by analysts.
D. mid-December, with the intent to sell in early January.
-
Question 1477:
Caleb Gold is studying for the Level 1 CFA examination with a fellow group of first year MBA students at the London School of Economics. During that night's study session, Stephan LeMond, the self-proclaimed group "leader," gives a short presentation on the forms of the efficient market hypothesis (EMH). As Gold listens, he hears LeMond make an obviously incorrect statement. He quickly speaks up, and identifies which of the following statements as INCORRECT?
A. The weak-form EMH states that stock prices reflect current public market information and expectations.
B. The semi-strong form EMH addresses market and non-market public information.
C. The strong-form EMH assumes perfect markets.
D. The weak-form EMH suggests that technical analysis will not provide excess returns while the semi-strong form suggests that fundamental analysis cannot achieve excess returns.
-
Question 1478:
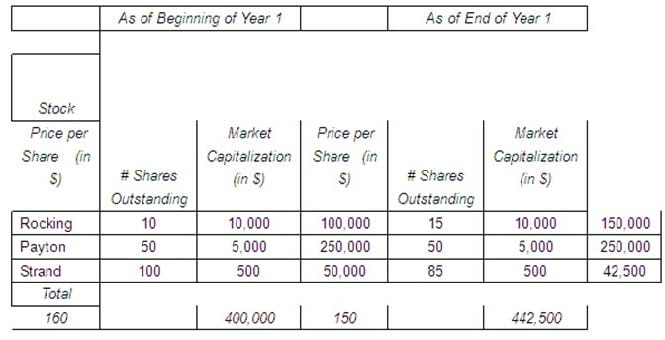
The table below lists information on price per share and shares outstanding for three stocks ?Rocking, Payton, and Strand.
Using the information in the table, calculate the value of a market-value weighted index at year-end and the one-year return on the price-weighted index. The beginning value for the market index is 100. (Note: The choices are listed in the order market-value weighted index value and price-weighted index percent return, respectively). Which of the following choices is closest to the correct answer?
A. 10.6, 6.3.
B. 110.6, -6.3.
C. 110.6, 50.0.
D. 10.6, 8.4.
-
Question 1479:
Using the following assumptions, calculate the rate of return on a margin transaction and the stock price at
which the investor who purchases the stock will receive a margin call.
What of the following choices is closest to the correct answer? The margin transaction return is:
A. 83.33%, and the investor will receive a margin call at a stock price of $15.43.
B. 33.33%, and the investor will receive a margin call at a stock price of $15.43.
C. 111.11%, and the investor will receive a margin call at a stock price of $21.00.
D. 111.11%, and the investor will receive a margin call at a stock price of $15.43.
-
Question 1480:
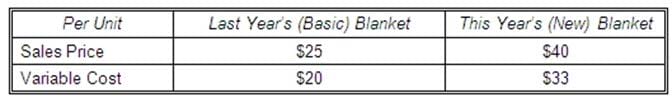
Annah Korotkin is the sole proprietor of CoverMeUp, a business that designs and sews outdoor clothing for dogs. Each year, she rents a booth at the regional Pet Expo and sells only blankets. Korotkin views the Expo as primarily a marketing tool and is happy to break even (that is, cover her booth rental). For the last 3 years, she has sold exactly enough blankets to cover the $750 booth rental fee. This year, she decided to make all blankets for the Expo out of high-tech waterproof/breathable material that is more expensive to produce, but that she believes she can sell for a higher profit margin. Information on the two types of blankets is as follows: Assuming that Korotkin remains most interested in covering the booth cost (which has increased to $840), how many more or fewer blankets (new style) does she need to sell to cover the booth cost? To cover this year's booth costs, Korotkin needs to sell:
A. 42 more blankets than last year.
B. 42 fewer blankets than last year.
C. 30 fewer blankets than last year.
D. the same amount of blankets as last year.
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only CFA Institute exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your CFA-LEVEL-1 exam preparations and CFA Institute certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.