Exam Details
Exam Code
:2VB-601Exam Name
:VMware Specialist: vSAN 6.xCertification
:VMware CertificationsVendor
:VMwareTotal Questions
:109 Q&AsLast Updated
:Dec 22, 2024
VMware VMware Certifications 2VB-601 Questions & Answers
-
Question 51:
Which statement is true about vSAN three-node cluster configuration?
A. Three-node clusters can tolerate a maximum of 2 host failures as long as there are at least 2 disk groups in each host.
B. A storage policy with a RAID-5/6 erasure coding rule cannot be applied to a virtual machine object.
C. A storage policy with a deduplication and compression rule can be applied to a virtual machine object.
D. Three-node clusters can tolerate a maximum of 2 host failures.
-
Question 52:
An administrator is deploying vSAN 6.6.
What must the administrator configure to set up vSAN networking?
A. IGMP snooping on the switch
B. A class A network address
C. A matching subnet mask on all vSAN VMkernel ports
D. A vSAN VMkernel port on each host in the cluster
-
Question 53:
The following are the configuration details of a 12-node all-flash VSAN cluster:
1.
Every node has one disk group
2.
Each disk group consists of one cache device and six capacity devices
Which two methods can be used to increase the size of the cache tier in each host? (Choose two.)
A. Promote a capacity device to a cache device so that each disk group has two cache devices.
B. Add a new cache device to the host. Reconfigure the host to have two disk groups with one cache device and three capacity devices per disk group.
C. Add a second cache device to each disk group.
D. Replace the existing cache device in each disk group with a larger cache device.
-
Question 54:
Which VMware-recommended tool provides specific information on the best strategy for a vSAN deployment?
A. vSAN VIP Assessment Tool
B. vSAN TCO and Sizing Calculator
C. vSAN Health Check UI
D. vSAN ReadyNode Configurator
-
Question 55:
How many consecutive heartbeats of communication must be lost between master and the witness host for the witness host to be deemed to have failed?
A. 5
B. 7
C. 3
D. 10
-
Question 56:
Which two factors below determine how a VMDK object will be split on a vSAN cluster? (Choose two.)
A. Checksum parameter
B. Free capacity in the cache tier devices
C. Size of the VMDK object
D. Stripe width parameter
-
Question 57:
Exhibit:
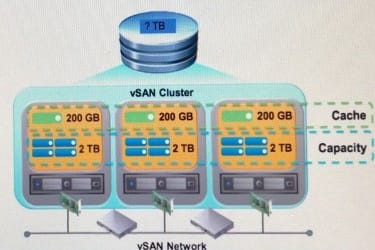
View the exhibit.
The following are configuration details for a three-node all-flash vSAN cluster
1.
Each node is identical in number of drives and disk controllers
2.
Each node has 4 x 500 GB SSD Capacity Tier, 1 x 200 GB SSD cache tier
What is the raw capacity of this cluster as configured?
A. 6.6 TB
B. 3 TB
C. 6 TB
D. 4 TB
-
Question 58:
For a hybrid vSAN configuration, the SSD resides in which tier?
A. Read tier
B. Write tier
C. Cache tier
D. Capacity tier
-
Question 59:
If the Primary level of failures to tolerate policy is changed from 2 to 3 without shutting down the virtual machine, what will happen when the policy is applied?
A. It will fail with an alert. Primary level of failures to tolerate=3 is not supported with mirroring.
B. It will fail with an alert. The policy of a running VM cannot be dynamically changed.
C. vSAN will try to create an additional mirror of the VM's disk components, as long as there is a sufficient number of fault domains and available capacity.
D. vSAN will switch its failure to tolerate method for any VMs with that policy, to optimize for space. Primary level of failures to tolerate=3 can only be accomplished with erasure coding.
-
Question 60:
An administrator is designing a vSAN cluster for a number of new workloads. The design calls for the use of erasure coding with RAID 5.
Which statement is true about what is needed to meet the needs of this scenario?
A. vSAN Standard licensing is sufficient
B. vSAN Enterprise licensing is required
C. An all-flash configuration is required.
D. Six nodes are required at a minimum.
Related Exams:
1V0-21.20
Associate VMware Data Center Virtualization1V0-31.21
Associate VMware Cloud Management and Automation1V0-41.20
Associate VMware Network Virtualization1V0-61.21
Associate VMware Digital Workspace1V0-71.21
Associate VMware Application Modernization1V0-81.20
Associate VMware Security2V0-11.24
VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2 Administrator2V0-11.25
VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2 Administrator2V0-13.24
VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2 Architect2V0-21.20
Professional VMware vSphere 7.x
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only VMware exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your 2VB-601 exam preparations and VMware certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.