MULESOFT-INTEGRATION-ARCHITECT-I Exam Details
-
Exam Code
:MULESOFT-INTEGRATION-ARCHITECT-I -
Exam Name
:Salesforce Certified MuleSoft Integration Architect I -
Certification
:Salesforce Certifications -
Vendor
:Salesforce -
Total Questions
:273 Q&As -
Last Updated
:Jan 24, 2026
Salesforce MULESOFT-INTEGRATION-ARCHITECT-I Online Questions & Answers
-
Question 1:
According to MuleSoft, which deployment characteristic applies to a microservices application architecture?
A. Services exist as independent deployment artifacts and can be scaled -independently of other services
B. All services of an application can be deployed together as single Java WAR file
C. A deployment to enhance one capability requires a redeployment of all capabilities
D. Core business capabilities are encapsulated in a single, deployable application -
Question 2:
An integration Mute application is being designed to process orders by submitting them to a backend system for offline processing. Each order will be received by the Mute application through an HTTPS POST and must be acknowledged immediately. Once acknowledged, the order will be submitted to a backend system. Orders that cannot be successfully submitted due to rejections from the backend system will need to be processed manually (outside the backend system).
The Mule application will be deployed to a customer-hosted runtime and is able to use an existing ActiveMQ broker if needed.
The backend system has a track record of unreliability both due to minor network connectivity issues and longer outages.
What idiomatic (used for their intended purposes) combination of Mule application components and ActiveMQ queues are required to ensure automatic submission of orders to the backend system, while minimizing manual order processing?
A. An On Error scope Non-persistent VM ActiveMQ Dead Letter Queue for manual processing
B. An On Error scope MuleSoft Object Store ActiveMQ Dead Letter Queue for manual processing
C. Until Successful component MuleSoft Object Store ActiveMQ is NOT needed or used
D. Until Successful component ActiveMQ long retry Queue ActiveMQ Dead Letter Queue for manual processing -
Question 3:
A leading bank implementing new mule API.
The purpose of API to fetch the customer account balances from the backend application and display them on the online platform the online banking platform. The online banking platform will send an array of accounts to Mule API get the account balances.
As a part of the processing the Mule API needs to insert the data into the database for auditing purposes and this process should not have any performance related implications on the account balance retrieval flow
How should this requirement be implemented to achieve better throughput?
A. Implement the Async scope fetch the data from the backend application and to insert records in the Audit database
B. Implement a for each scope to fetch the data from the back-end application and to insert records into the Audit database
C. Implement a try-catch scope to fetch the data from the back-end application and use the Async scope to insert records into the Audit database
D. Implement parallel for each scope to fetch the data from the backend application and use Async scope to insert the records into the Audit database -
Question 4:
A Mule application currently writes to two separate SQL Server database instances across the internet using a single XA transaction. It is 58. proposed to split this one transaction into two separate non-XA transactions with no other changes to the Mule application.
What non-functional requirement can be expected to be negatively affected when implementing this change?
A. Throughput
B. Consistency
C. Response time
D. Availability -
Question 5:
A Mule application is synchronizing customer data between two different database systems.
What is the main benefit of using eXtended Architecture (XA) transactions over local transactions to synchronize these two different database systems?
A. An XA transaction synchronizes the database systems with the least amount of Mule configuration or coding
B. An XA transaction handles the largest number of requests in the shortest time
C. An XA transaction automatically rolls back operations against both database systems if any operation falls
D. An XA transaction writes to both database systems as fast as possible -
Question 6:
A travel company wants to publish a well-defined booking service API to be shared with its business partners. These business partners have agreed to ONLY consume SOAP services and they want to get the service contracts in an easily consumable way before they start any development. The travel company will publish the initial design documents to Anypoint Exchange, then share those documents with the business partners.
When using an API-led approach, what is the first design document the travel company should deliver to its business partners?
A. Create a WSDL specification using any XML editor
B. Create a RAML API specification using any text editor
C. Create an OAS API specification in Design Center
D. Create a SOAP API specification in Design Center -
Question 7:
Refer to the exhibit.
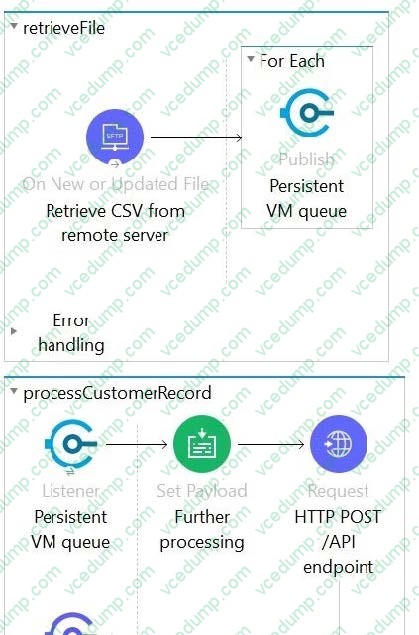
This Mule application is deployed to multiple Cloudhub workers with persistent queue enabled. The retrievefile flow event source reads a CSV file from a remote SFTP server and then publishes each record in the CSV file to a VM queue. The processCustomerRecords flow's VM Listner receives messages from the same VM queue and then processes each message separately.
How are messages routed to the cloudhub workers as messages are received by the VM Listener?
A. Each message is routed to ONE of the Cloudhub workers in a DETERMINSTIC round robin fashion thereby EXACTLY BALANCING messages among the cloudhub workers
B. Each messages routes to ONE of the available Clouhub workers in a NON-DETERMINSTIC non round-robin fashion thereby APPROXIMATELY BALANCING messages among the cloudhub workers
C. Each message is routed to the SAME Cloudhub worker that retrieved the file, thereby BINDING ALL messages to ONLY that ONE Cloudhub worker
D. Each message is duplicated to ALL of the Cloudhub workers, thereby SHARING EACH message with ALL the Cloudhub workers. -
Question 8:
As a part of design , Mule application is required call the Google Maps API to perform a distance computation. The application is deployed to cloudhub.
At the minimum what should be configured in the TLS context of the HTTP request configuration to meet these requirements?
A. The configuration is built-in and nothing extra is required for the TLS context
B. Request a private key from Google and create a PKCS12 file with it and add it in keyStore as a part of TLS context
C. Download the Google public certificate from a browser, generate JKS file from it and add it in key store as a part of TLS context
D. Download the Google public certificate from a browser, generate a JKS file from it and add it in Truststore as part of the TLS context -
Question 9:
Which Salesforce API is invoked to deploy, retrieve, create, update, or delete customization information, such as custom object definitions using Mule Salesforce Connectors in a Mule application?
A. sObject Platform Action API
B. User Interface API
C. Metadata API
D. Process Rules API -
Question 10:
An organization is evaluating using the CloudHub shared Load Balancer (SLB) vs creating a CloudHub dedicated load balancer (DLB). They are evaluating how this choice affects the various types of certificates used by CloudHub deplpoyed Mule applications, including MuleSoft-provided, customer-provided, or Mule application-provided certificates.
What type of restrictions exist on the types of certificates that can be exposed by the CloudHub Shared Load Balancer (SLB) to external web clients over the public internet?
A. Only MuleSoft-provided certificates are exposed.
B. Only customer-provided wildcard certificates are exposed.
C. Only customer-provided self-signed certificates are exposed.
D. Only underlying Mule application certificates are exposed (pass-through)
Related Exams:
-
201-COMMERCIAL-BANKING-FUNCTIONAL
Salesforce enCino 201 Commercial Banking Functional -
ADM-201
Administration Essentials for New Admins -
ADM-211
Administration Essentials for Experienced Admin -
ADVANCED-ADMINISTRATOR
Salesforce Certified Advanced Administrator -
ADX-201
Administrative Essentials for New Admins in Lightning Experience -
ADX-271
Salesforce Certified Community Cloud Consultant -
AGENTFORCE-SPECIALIST
Salesforce Certified Agentforce Specialist (AI-201) -
ANC-301
Working with Data and Dashboards in Einstein Analytics -
AP-223
CPQ and Billing Consultant Accredited Professional (AP-223) -
B2B-COMMERCE-ADMINISTRATOR
Salesforce Accredited B2B Commerce Administrator
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Salesforce exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your MULESOFT-INTEGRATION-ARCHITECT-I exam preparations and Salesforce certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.