Exam Details
Exam Code
:MCAT-TESTExam Name
:Medical College Admission Test: Verbal Reasoning, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences, Writing SampleCertification
:Medical Tests CertificationsVendor
:Medical TestsTotal Questions
:812 Q&AsLast Updated
:Aug 12, 2025
Medical Tests Medical Tests Certifications MCAT-TEST Questions & Answers
-
Question 41:
Researchers are currently trying to develop materials which could be used to replace damaged or destroyed human muscle tissue. One of the more promising avenues of research involves the use of substances that contract with the application of a small electric current.
Two physicists published an article relating to their work with Substance Q42, a material which contracts with the application of very small electric currents.
The atomic structure of the substance, they report, is designed so that the magnetic fields from each atom maintain a certain distance between adjacent atoms. With the application of an electrical current, the atoms' magnetic fields are
dampened slightly, causing them to draw closer together. The extent to which it contracts is dependent upon the strength of the current passing through it, but will at any rate never exceed a 20% reduction in length.
Moreover, the physicists report, Substance Q42 essentially operated like a spring, but one which can compress itself. The force generated by a spring, Fs, is given by the following equation:
Fs = -kx,
where k is the spring of constant in N/m, and x is the distance of compression (or expansion, but that is irrelevant for this example, since Substance Q42 only compresses).
With this in mind, it is possible to calculate the feasibility of using Substance Q42 as a replacement for human muscle tissue. Assume a section of test Substance Q42 is hooked to a scalable electrical source. The section is 10 cm long at its
fully extended state, and 8 cm long when fully compressed due to an electrical current.
If k = 40 000 N/m, then how much work does Substance Q42 do in compressing from its relaxed length to a length of 9 cm?
A. 2 J
B. 20 J
C. 40 J
D. 100 J
-
Question 42:
Researchers are currently trying to develop materials which could be used to replace damaged or destroyed human muscle tissue. One of the more promising avenues of research involves the use of substances that contract with the application of a small electric current.
Two physicists published an article relating to their work with Substance Q42, a material which contracts with the application of very small electric currents.
The atomic structure of the substance, they report, is designed so that the magnetic fields from each atom maintain a certain distance between adjacent atoms. With the application of an electrical current, the atoms' magnetic fields are
dampened slightly, causing them to draw closer together. The extent to which it contracts is dependent upon the strength of the current passing through it, but will at any rate never exceed a 20% reduction in length.
Moreover, the physicists report, Substance Q42 essentially operated like a spring, but one which can compress itself. The force generated by a spring, Fs, is given by the following equation:
Fs = -kx,
where k is the spring of constant in N/m, and x is the distance of compression (or expansion, but that is irrelevant for this example, since Substance Q42 only compresses).
With this in mind, it is possible to calculate the feasibility of using Substance Q42 as a replacement for human muscle tissue. Assume a section of test Substance Q42 is hooked to a scalable electrical source. The section is 10 cm long at its
fully extended state, and 8 cm long when fully compressed due to an electrical current.
Substance Q42 is fully expanded and then contracts in response to a 5.0 amp current. Which of the following best represents the conversion of energies in the process described?
A. Potential --> kinetic --> mechanical
B. Potential --> mechanical --> kinetic
C. Electrical --> mechanical --> potential
D. Potential --> mechanical --> electrical
-
Question 43:
Researchers are currently trying to develop materials which could be used to replace damaged or destroyed human muscle tissue. One of the more promising avenues of research involves the use of substances that contract with the application of a small electric current.
Two physicists published an article relating to their work with Substance Q42, a material which contracts with the application of very small electric currents.
The atomic structure of the substance, they report, is designed so that the magnetic fields from each atom maintain a certain distance between adjacent atoms. With the application of an electrical current, the atoms' magnetic fields are
dampened slightly, causing them to draw closer together. The extent to which it contracts is dependent upon the strength of the current passing through it, but will at any rate never exceed a 20% reduction in length.
Moreover, the physicists report, Substance Q42 essentially operated like a spring, but one which can compress itself. The force generated by a spring, Fs, is given by the following equation:
Fs = -kx,
where k is the spring of constant in N/m, and x is the distance of compression (or expansion, but that is irrelevant for this example, since Substance Q42 only compresses).
With this in mind, it is possible to calculate the feasibility of using Substance Q42 as a replacement for human muscle tissue. Assume a section of test Substance Q42 is hooked to a scalable electrical source. The section is 10 cm long at its
fully extended state, and 8 cm long when fully compressed due to an electrical current.
If an artificial arm muscle must be capable of doing 8 J work in 0.5 seconds time in order to efficiently substitute for human tissue, what average power must the section of Substance Q42 be capable of?
A. 16 Watts
B. 22 Watts
C. 32 Watts
D. 36 Watts
-
Question 44:
Researchers are currently trying to develop materials which could be used to replace damaged or destroyed human muscle tissue. One of the more promising avenues of research involves the use of substances that contract with the application of a small electric current.
Two physicists published an article relating to their work with Substance Q42, a material which contracts with the application of very small electric currents.
The atomic structure of the substance, they report, is designed so that the magnetic fields from each atom maintain a certain distance between adjacent atoms. With the application of an electrical current, the atoms' magnetic fields are
dampened slightly, causing them to draw closer together. The extent to which it contracts is dependent upon the strength of the current passing through it, but will at any rate never exceed a 20% reduction in length.
Moreover, the physicists report, Substance Q42 essentially operated like a spring, but one which can compress itself. The force generated by a spring, Fs, is given by the following equation:
Fs = -kx,
where k is the spring of constant in N/m, and x is the distance of compression (or expansion, but that is irrelevant for this example, since Substance Q42 only compresses).
With this in mind, it is possible to calculate the feasibility of using Substance Q42 as a replacement for human muscle tissue. Assume a section of test Substance Q42 is hooked to a scalable electrical source. The section is 10 cm long at its
fully extended state, and 8 cm long when fully compressed due to an electrical current. How much force does the section apply when it compresses from rest state to 9.5 cm in length? k = 40 000 N/m
A. 100 N
B. 200 N
C. 500 N
D. 1000 N
-
Question 45:
Arginine is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. Most healthy people do not need to supplement with arginine because the body usually produces sufficient quantities. The pathway for arginine synthesis was studied using cells from a red bread mold. This natural form of arginine is illustrated below.
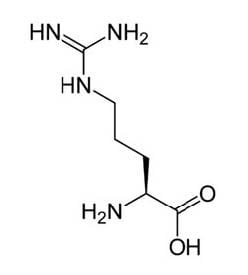
The red bread mold Neurospora crassa grows well on a cultural plate with "minimal" medium which is a fluid containing only a few simple sugars, inorganic salts, and vitamin. Neurospora that grows normally in nature (wild type) has enzymes that convert these simple substances into the amino acids necessary for growth. Mutating any one of the genes that makes an enzyme can produce a Neurospora strain that cannot grow on minimal medium. The mutant would only grow if the enzyme product were to be added as a supplement. On the other hand, if a "complete" medium is provided, containing all required amino acids, then Neurospora would grow, with or without mutation.

Figure 1 A synthesis pathway for the amino acid arginine. Each gene in italics in the diagram produces one enzyme necessary for the synthesis of this essential amino acid required for growth.
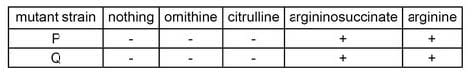
Table 1 Growth response of mutant strains in "minimal" media with supplements (ornithine, citrulline, argininosuccinate, and arginine) as indicated. Strain growth is indicated by (+) and no strain growth is indicated by (-). Consider tetrapeptides containing 2 equivalents each of the natural forms of arginine and proline. How many different linear tetrapeptides can be synthesized?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 6
D. 8
-
Question 46:
Researchers are currently trying to develop materials which could be used to replace damaged or destroyed human muscle tissue. One of the more promising avenues of research involves the use of substances that contract with the application of a small electric current.
Two physicists published an article relating to their work with Substance Q42, a material which contracts with the application of very small electric currents.
The atomic structure of the substance, they report, is designed so that the magnetic fields from each atom maintain a certain distance between adjacent atoms. With the application of an electrical current, the atoms' magnetic fields are
dampened slightly, causing them to draw closer together. The extent to which it contracts is dependent upon the strength of the current passing through it, but will at any rate never exceed a 20% reduction in length.
Moreover, the physicists report, Substance Q42 essentially operated like a spring, but one which can compress itself. The force generated by a spring, Fs, is given by the following equation:
Fs = -kx,
where k is the spring of constant in N/m, and x is the distance of compression (or expansion, but that is irrelevant for this example, since Substance Q42 only compresses).
With this in mind, it is possible to calculate the feasibility of using Substance Q42 as a replacement for human muscle tissue. Assume a section of test Substance Q42 is hooked to a scalable electrical source. The section is 10 cm long at its
fully extended state, and 8 cm long when fully compressed due to an electrical current.
A force-meter is attached to one end of a section of Substance Q42; the other end of the section is secured to a non-moving surface. When fully compressed, the force-meter registers a force exerted by the section of 250 N. What is the
spring constant?
A. 12 500 N/m
B. 12 800 N/m
C. 16 700 N/m
D. 20 500 N/m
-
Question 47:
Arginine is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. Most healthy people do not need to supplement with arginine because the body usually produces sufficient quantities. The pathway for arginine synthesis was studied using cells from a red bread mold. This natural form of arginine is illustrated below.

The red bread mold Neurospora crassa grows well on a cultural plate with "minimal" medium which is a fluid containing only a few simple sugars, inorganic salts, and vitamin. Neurospora that grows normally in nature (wild type) has enzymes that convert these simple substances into the amino acids necessary for growth. Mutating any one of the genes that makes an enzyme can produce a Neurospora strain that cannot grow on minimal medium. The mutant would only grow if the enzyme product were to be added as a supplement. On the other hand, if a "complete" medium is provided, containing all required amino acids, then Neurospora would grow, with or without mutation.

Figure 1 A synthesis pathway for the amino acid arginine. Each gene in italics in the diagram produces one enzyme necessary for the synthesis of this essential amino acid required for growth. Table 1 Growth response of mutant strains in "minimal" media with supplements (ornithine, citrulline, argininosuccinate, and arginine) as indicated. Strain growth is indicated by (+) and no strain growth is indicated by (-).

Experiments using the two mutant strains P and Q, reveal that strain P accumulates citrulline, but strain Q does not. Which of the following statements is most consistent with the data provided?
A. Strain Q has only one mutation.
B. Strain P has a mutation in argF only.
C. Strain P has mutations in argF, argG and argH.
D. Strain P has a mutation in argG only.
-
Question 48:
Arginine is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. Most healthy people do not need to supplement with arginine because the body usually produces sufficient quantities. The pathway for arginine synthesis was studied using cells from a red bread mold. This natural form of arginine is illustrated below.

The red bread mold Neurospora crassa grows well on a cultural plate with "minimal" medium which is a fluid containing only a few simple sugars, inorganic salts, and vitamin. Neurospora that grows normally in nature (wild type) has enzymes that convert these simple substances into the amino acids necessary for growth. Mutating any one of the genes that makes an enzyme can produce a Neurospora strain that cannot grow on minimal medium. The mutant would only grow if the enzyme product were to be added as a supplement. On the other hand, if a "complete" medium is provided, containing all required amino acids, then Neurospora would grow, with or without mutation.

Figure 1 A synthesis pathway for the amino acid arginine. Each gene in italics in the diagram produces one enzyme necessary for the synthesis of this essential amino acid required for growth.

Table 1 Growth response of mutant strains in "minimal" media with supplements (ornithine, citrulline, argininosuccinate, and arginine) as indicated. Strain growth is indicated by (+) and no strain growth is indicated by (-). Which of the following is most likely consistent with the overall synthetic pathway for arginine (accounting for coupled reactions)?
A. H < 0
B. G = 0
C. net ATP production
D. G > 0
-
Question 49:
Arginine is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. Most healthy people do not need to supplement with arginine because the body usually produces sufficient quantities. The pathway for arginine synthesis was studied using cells from a red bread mold. This natural form of arginine is illustrated below.

The red bread mold Neurospora crassa grows well on a cultural plate with "minimal" medium which is a fluid containing only a few simple sugars, inorganic salts, and vitamin. Neurospora that grows normally in nature (wild type) has enzymes that convert these simple substances into the amino acids necessary for growth. Mutating any one of the genes that makes an enzyme can produce a Neurospora strain that cannot grow on minimal medium. The mutant would only grow if the enzyme product were to be added as a supplement. On the other hand, if a "complete" medium is provided, containing all required amino acids, then Neurospora would grow, with or without mutation.

Figure 1 A synthesis pathway for the amino acid arginine. Each gene in italics in the diagram produces one enzyme necessary for the synthesis of this essential amino acid required for growth.

Table 1 Growth response of mutant strains in "minimal" media with supplements (ornithine, citrulline, argininosuccinate, and arginine) as indicated. Strain growth is indicated by (+) and no strain growth is indicated by (-).
According to the information provided, a conclusion that can be made with certainty is that neither mutant strain P nor Q have the defective enzyme:
A. carbamoyltransferase.
B. argininosuccinate synthase.
C. argininosuccinase.
D. None of the above enzymes are defective in either mutant strain P nor Q.
-
Question 50:
In order to determine the Doppler shift in perceived sound frequency, the following variables must be known:
speed of sound in medium time of interaction between sound source and detector distance between source and detector frequency of emitted sound
A. I only
B. I and III
C. II and IV
D. I an IV
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Medical Tests exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your MCAT-TEST exam preparations and Medical Tests certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.