JN0-649 Exam Details
-
Exam Code
:JN0-649 -
Exam Name
:Enterprise Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-ENT) -
Certification
:Juniper Certifications -
Vendor
:Juniper -
Total Questions
:65 Q&As -
Last Updated
:Jan 26, 2026
Juniper JN0-649 Online Questions & Answers
-
Question 1:
You are deploying IP phones in your enterprise networks. When plugged in, the IP phones mustbe automatically provided with the correct VLAN ID needed for sending voice traffic to the EX Series switches.
In this scenario, which two solutions are required to accomplish this task? (Choose two.)
A. Enable LLDP-MED on appropriate access interfaces.
B. Create two VLANs and assign them as VLAN members to the appropriate access interfaces.
C. Enable the voice VLAN feature with the appropriate access interfaces and VLAN ID for voice traffic.
D. Use LLDP on appropriate interfaces. -
Question 2:
Your network has an unmanaged switch between the hosts and your EX Series switch. After the traffic enters theEX Series switch, each host must be on a separate VLAN.
How would you accomplish this task?
A. Configure an input firewall filter on interface ge-0/0/3 to match the source MAC or IP address of the hosts to assign the VLANs.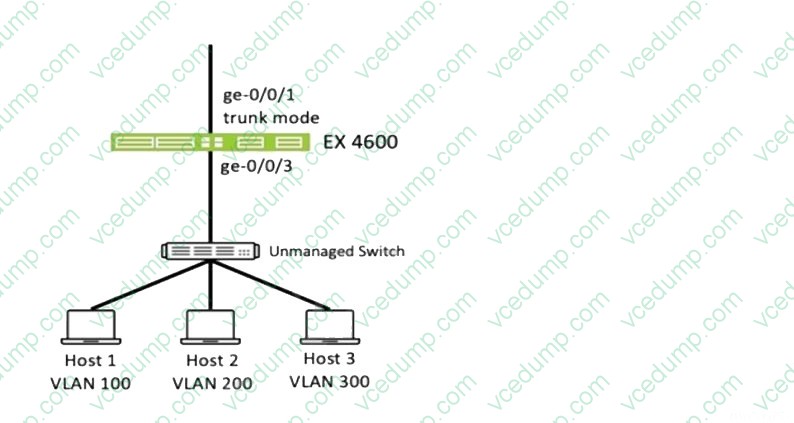
B. Configure an output firewall filter on interface ge-0/0/1 to match the destination MAC or IP address of the hosts to assign the VLANs.
C. Configure interface ge-0/0/3 to a mode trunk to assign the VLANs.
D. Configure VSTP on interface ge-0/0/1 to assign the VLANs. -
Question 3:
Your network is multihomed to two ISPs. The BGP sessions are established; however, the ISP peers are not receiving any routes.
Which two statements are correct about troubleshooting your configuration? (Choose two.)
A. Verify the import policies on your router.
B. Verify that the BGP routes are active in your routing table.
C. Verify the export policies on your router.
D. Verity that the multihop settings are configured on your router. -
Question 4:
BGP multipath or multihop are not configured in your network.
In this scenario, what is the correct sequence for BGP active route selection?
A. higher local preference shortest AS path lowest peer address lowest router ID lower origin code
B. higher local preference shortest AS path lower origin code lowest router ID lowest peer address
C. higher local preference lowest router ID lowest peer address lower origin code shortest AS path
D. higher local preference shortest AS path lowest router ID lowest peer address lower origin code -
Question 5:
Which statement is correct about IS-IS?
A. IS-IS uses areas and an autonomous system.
B. Level 1/2 routers automatically inject a default route to the nearest Level 1 router.
C. Level 2 routers must share the same area address.
D. Level 1 routers route traffic between autonomous systems. -
Question 6:
Your enterprise network is running BGP VPNs to support multitenancy. Some of the devices with which you peer BGP do not support the VPN NLRI. You must ensure that you do not send BGP VPN routes to the remote peer.
Which two configuration steps will satisfy this requirement? (Choose two.)
A. Configure an import policy on the remote peer to reject the routes when they are received.
B. Configure an export policy on the local BGP peer to reject the VPN routes being sent to the remote peer.
C. Configure a route reflector for the VPN NLRI.
D. Configure the apply-vpn-export feature on the local BGP peer. -
Question 7:
A BGP network has been designed to provide resiliency and redundancy to a multihomed customer network.
Which two statements are correct in this scenario? (Choose two.)
A. Both the next hops will be used to forward traffic to R2.
B. A routing policy will be required to forward traffic to both next hops.
C. The TTL value of 1 is set to limit the scope of the EBGP session.
D. The ttl statement must be configuredto accommodate peering to a loopback address of a directly connected peer. -
Question 8:
There are two BGP routes to 10.200.200.0/24 received from twoexternal peers. Route 1 comes from a neighbor with a router ID of 10.10.100.1 and a peer IP address of 10.10.30.1, and route 2 comes from a neighbor with a router ID of
10.10.200.1 and a peer IP address of 10.10.50.1. Both routes have the same MED value, origin value, AS path length, and local preference number.
In this scenario, which statement is correct about the active route?
A. Route 1 will be active because of the peer IP address.
B. Route 2 will be active because of the peer IP address.
C. Route 1 will be active because of the router ID.
D. Route 2 will be active because of the router ID. -
Question 9:
You are troubleshooting an EVPN-VXLAN IP fabric and observe the loop shown in the exhibit. Which two steps would you take to further troubleshoot this problem? (Choose two.)
A. Verify that the same ESI is configured on the link from thehost and that it matches the source.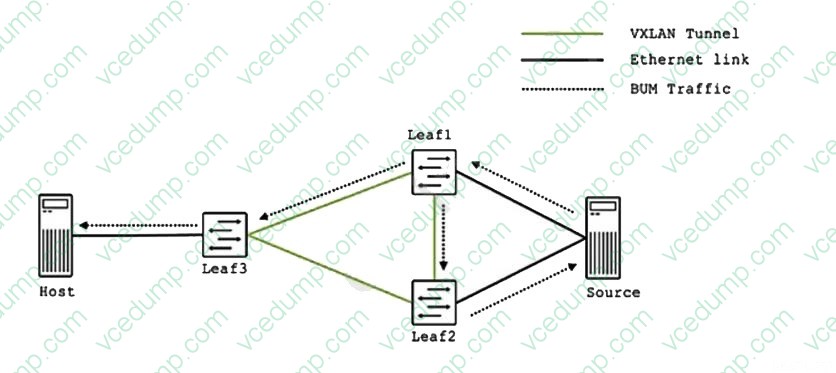
B. Issue the show route table bgp.evpn.0 command on Leaf2 and verify that Type 4 routes are present.
C. Issue the show route table bgp.evpn.0 command on Leaf2 and verify that Type 3 routes are present.
D. Verify thatthe same ESI is configured on the two links from the source. -
Question 10:
You want to create an OSPF area that only contains intra-area route information in the form of Type 1 and Type 2 LSAs.
In this scenario, which area is needed to accomplish this task?
A. totally non-to-stubby area
B. totally stubby area
C. stub area
D. non-to-stubby area
Related Exams:
-
JN0-102
Internet Associate, Junos(JNCIA-Junos) -
JN0-104
Junos, Associate (JNCIA-Junos) -
JN0-105
Junos, Associate (JNCIA-Junos) -
JN0-1101
Juniper Networks Certified Design Associate (JNCDA) -
JN0-1103
Design, Associate (JNCIA-Design) -
JN0-130
Juniper networks Certified internet specialist.e(jncis-e) -
JN0-1301
Data Center Design, Specialist (JNCDS-DC) -
JN0-1302
Data Center Design Specialist (JNCDS-DC) -
JN0-1331
Security Design, Specialist (JNCDS-SEC) -
JN0-1332
Security Design, Specialist (JNCDS-SEC)
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Juniper exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your JN0-649 exam preparations and Juniper certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.