Exam Details
Exam Code
:IMANET-CMAExam Name
:Certified Management Accountant (CMA)Certification
:IMANET CertificationsVendor
:IMANETTotal Questions
:1336 Q&AsLast Updated
:Jul 11, 2025
IMANET IMANET Certifications IMANET-CMA Questions & Answers
-
Question 231:
Whitehall Corporation produces chemicals used in the cleaning industry. During the previous month, Whitehall incurred $300,000 of joint costs in producing 60,000 units of AM-12 and 40,000 units of BM-36. Whitehall uses the units-of-production method to allocate joint costs. Currently, AM-12 is sold at split-off for $3.50 per unit. Flank Corporation has approached Whitehall to purchase all of the production of AM-12 after further processing. The further processing will cost Whitehall $90,000. Concerning AM- 12, which one of the following alternatives is most advantageous?
A. Whitehall should process further and sell to Flank if the total selling price per unit after further processing is greater than $3.00, which covers the joint costs.
B. Whitehall should continue to sell at split-off unless Flank offers at least $4.50 per unit after further processing, which covers Whitehall's total costs.
C. Whitehall should process further and sell to Flank if the total selling price per unit after further processing is greater than $5.00.
D. Whitehall should process further and sell to Flank if the total selling price per unit after further processing is greater than $5.25, which maintains the same gross profit percentage.
-
Question 232:
N-Air Corporation uses a joint process to produce three products: A, B, and C, all derived from one input. The company can sell these . products at the point of split-off (end of the joint process) or process them further. The joint production costs during October were $10,000. N-Air allocates joint costs to the products in proportion to the relative physical volume of output. Additional information is presented in the opposite column.
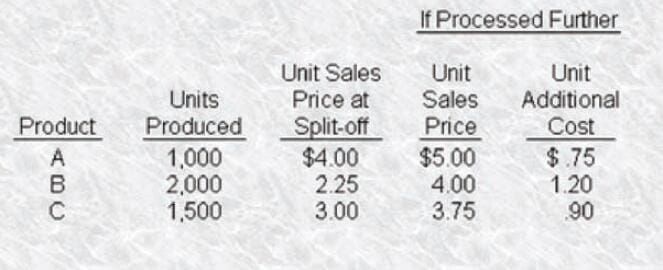
Assuming sufficient demand exists, N-Air could sell all the products at the prices previously mentioned at either the split-off point or after further processing. To maximize its profits, N-Air Corporation should
A. Sell product A at split-oft and perform additional processing on products B and C.
B. Sell product B at split-oft and perform additional processing on products C and A.
C. Sell product C at split-off and perform additional processing on products A and B.
D. Sell products A, B, and C at split-off.
-
Question 233:
N-Air Corporation uses a joint process to produce three products: A, B, and C, all derived from one input. The company can sell these . products at the point of split-off (end of the joint process) or process them further. The joint production costs during October were $10,000. N-Air allocates joint costs to the products in proportion to the relative physical volume of output. Additional information is presented in the opposite column.

Assuming that all products were sold at the split-off point during October, the gross profit from the production process would be
A. $13,000
B. $10,000
C. $8,625
D. $3,000
-
Question 234:
Copeland Inc. produces X-547 in a joint manufacturing process. The company is studying whether to sell X-547 at the split-off point or upgrade the product to become Xylene. The following information has been gathered:
I. Selling price per pound of X-547 II. Variable manufacturing costs of upgrade process Ill. Avoidable fixed costs of upgrade process
IV.
Selling price per pound of Xylene
V.
Joint manufacturing costs to produce X-547
Which items should be reviewed when making the upgrade decision?
A. I, II, and IV only.
B. I, II, Ill, and IV only.
C. I, II, IV, and V only.
D. II and Ill only.
-
Question 235:
A firm produces two joint products (A and B) from one unit of raw material, which costs $1,000. Product A can be sold for $700 and product B can be sold for $500 at the split-off point. Alternatively, both A and/or B can be processed further and sold for $900 and $1 ,200, respectively. The additional processing costs are $100 for A and $750 for B. Should the firm process products A and B beyond the split-off point?
A. Both A and B should be processed further.
B. Only B should be processed further.
C. Only A should be processed further.
D. Neither product should be processed further.
-
Question 236:
In joint-product costing and analysis, which one of the following costs is relevant when deciding the point at which a product should be sold to maximize profits?
A. Separable costs after the split-off point.
B. Joint costs to the split-off point.
C. Sales salaries for the period when the units were produced.
D. Purchase costs of the materials required for the joint products.
-
Question 237:
Kator Co. is a manufacturer of industrial components. One of their products that is used as a subcomponent in auto manufacturing is KB-96. This product has the following financial structure per unit.

KatorCo. has received a special, one-time order for 1,000 KB-96 parts. Assume that Kator is operating at full capacity and that the contribution margin of the output that would be displaced by the special order is $10,000. Using the original data, the minimum price that is acceptable for this one-time special order is in excess of
A. $60
B. $70
C. $87
D. $100
-
Question 238:
Kator Co. is a manufacturer of industrial components. One of their products that is used as a subcomponent in auto manufacturing is KB-96. This product has the following financial structure per unit.

During the next year, KB-96 sales are expected to be 10000 units. All of the costs will remain the same except that fixed manufacturing overhead will increase by 20% and direct materials will increase by 10%. The selling price per unit for next year will be
A. $620.000
B. $750,000
C. $1,080,000
D. $1,110,000
-
Question 239:
Kator Co. is a manufacturer of industrial components. One of their products that is used as a subcomponent in auto manufacturing is KB-96. This product has the following financial structure per unit

Kator Co. has received a special, one-time order for 1,000 KB-96 parts. Assuming Kator has excess capacity, the minimum price that is acceptable for this one-time special order is in excess of
A. $47
B. $50
C. $60
D. $77
-
Question 240:
Which one of the following planning techniques is most likely to be used to determine which business units will receive additional capital and which will be divested?
A. Competitive strategies model.
B. Portfolio matrix analysis.
C. Scenario development.
D. Situational analysis.
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only IMANET exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your IMANET-CMA exam preparations and IMANET certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.