Exam Details
Exam Code
:IMANET-CMAExam Name
:Certified Management Accountant (CMA)Certification
:IMANET CertificationsVendor
:IMANETTotal Questions
:1336 Q&AsLast Updated
:Jul 11, 2025
IMANET IMANET Certifications IMANET-CMA Questions & Answers
-
Question 221:
Power Systems. Inc. manufactures jet engines for the United States armed forces on a cost-plus basis. The cost of a particular jet engine the company manufactures is shown as follows:

If production of this engine were discontinued1 the production capacity would be idle, and the supervisor would be laid off. When asked to bid on the next contract for this engine, the minimum unit price that Power Systems should bid is
A. $408,000
B. $365,000
C. $391,000
D. $385,000
-
Question 222:
Laurel Corporation has its own cafeteria with the following annual costs:

The overhead is 40% fixed. Of the fixed overhead, $25,000 is the salary of the cafeteria supervisor. The remainder of the fixed overhead has been allocated from total company overhead. Assuming the cafeteria supervisor will remain and Laurel will continue to pay his/her salary, the maximum cost Laurel will be willing to pay an outside firm to service the cafeteria is
A. $285,000
B. $175,000
C. $219,000
D. $241,000
-
Question 223:
In a make-versus-buy decision, the relevant costs include variable manufacturing costs as well as
A. Factory management costs.
B. General office costs.
C. Avoidable fixed costs.
D. Depreciation costs.
-
Question 224:
Listed below are a company's monthly unit costs to manufacture and market a particular product.

The company must decide to continue making the product or buy it from an outside supplier. The supplier has offered to make the product at the same level of quality that the company can make it. Fixed marketing costs would be unaffected, but variable marketing costs would be reduced by 30% if the company were to accept the proposal. What is the maximum amount per unit that the company can pay the supplier without decreasing operating income?
A. $8.50
B. $6.75
C. $7.75
D. $5.25
-
Question 225:
Polar Company sells refrigeration components both in the U.S. and to a subsidiary located in France. One
of the components, Part No. 456, has a variable manufacturing cost of $30. The part can be sold
domestically or shipped to the French subsidiary for use in the manufacture of a residential subassembly.
Relevant data with regard to Part No.
456 are shown below.

*
lf deemed preferable, these units could be sold in the U.S. Polar's applicable income tax rates are 40% in the U.S. and 70% in France.Polar will transfer Part No. 456 to the French subsidiary at either variable manufacturing cost or the domestic market price. On the basis of this information, which one of the following strategies should be recommended to Polar's management?
A.
Transfer 150,000 units at $30 and the French subsidiary pays the shipping costs.
B.
Transfer 150,000 units at $65 and the French subsidiary pays the shipping costs.
C.
Sell 150,000 units in the U.S. and the French subsidiary obtains Part No. 456 in France.
D.
Transfer 150,000 units at $65 and have the U.S. company absorb the shipping costs.
-
Question 226:
Condensed monthly operating income data for Korbin, Inc. for May follows: Additional information regarding Korbin's operations follows: One-fourth of each store's direct fixed costs would continue if either store is closed. Korbin allocates common fixed costs to each store on the basis of sales dollars. Management estimates that closing the Suburban Store would result in a 10% decrease in the Urban Store's sales, while closing the Urban Store would not affect the Suburban Store's sales. The operating results for May are representative of all months. One-half of the Suburban Store's dollar sales are from items sold at variable cost to attract customers to the store. Korbin is considering the deletion of these items, a move that would reduce the Suburban Store's direct fixed expenses by 15% and result in a 20% loss of Suburban Store's remaining sales volume. This change would not affect the Urban Store. A decision by Korbin to eliminate the items sold at cost would result in a monthly increase (decrease) in Korbin's operating income of
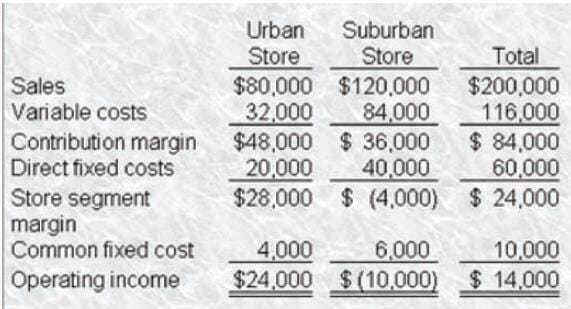
A. $(5,200)
B. $(1,200)
C. $(7,200)
D. $2,000
-
Question 227:
Condensed monthly operating income data for Korbin, Inc for May follows: Additional information regarding Korbin's operations follows: One-fourth of each store's direct fixed costs would continue if either store is closed. ?Korbin allocates common fixed costs to each store on the basis of sales dollars. Management estimates that closing the Suburban Store would result in a 10% decrease in the Urban Store's sales, while closing the Urban Store would not affect the Suburban Store's sales. The operating results for May are representative of all months. Korbin is considering a promotional campaign at the Suburban Store that would not affect the Urban Store. Increasing annual promotional expense at the Suburban Store by $60,000 in order to increase this store's sales by 10% would result in a monthly increase (decrease) in Korbin's operating income during the year (rounded) of

A. $(5000)
B. $(1400)
C. $487
D. $7,000
-
Question 228:
Condensed monthly operating income data for Korbin, Inc. for May follows

Additional information regarding Korbin's operations follows:
One-fourth of each store's direct fixed costs would continue if either store is closed.
Korbin allocates common fixed costs to each store on the basis of sales dollars.
Management estimates that closing the Suburban Store would result in a 10% decrease in the Urban
Store's sales, while closing the Urban Store would not affect the Suburban Store's sales.
The operating results for May are representative of all months. A decision by Korbin to close the Suburban
Store would result in a monthly increase (decrease) in Korbin's operating income of
A. $(10,800)
B. $(6,000)
C. $(1,200)
D. $4,000
-
Question 229:
When a multiproduct plant operates at full capacity, quite often decisions must be made as to which products to emphasize. These decisions are frequently made with a short-run focus. In making such decisions, managers should select products with the highest
A. Sales price per unit.
B. Individual unit contribution margin.
C. Sales volume potential.
D. Contribution margin per unit of the constraining resource.
-
Question 230:
Whitehall Corporation produces chemicals used in the cleaning industry During the previous month, Whitehall incurred $300,000 of joint costs in producing 60,000 units of AM-12 and 40000 units of BM-36. Whitehall uses the units-of-production method to allocate joint costs. Currently, AM-i 2 is sold at split-off for $3.50 per unit. Flank Corporation has approached Whitehall to purchase all of the production of AM-12 after further processing. The further processing will cost Whitehall $90000.Assume that Whitehall Corporation agreed to sell AM-12 to Flank Corporation for $5.50 per unit after further processing. During the first month of production, Whitehall sold 50,000 units with 10,000 units remaining in inventory at the end of the month. With respect to AM-12, which one of the following statements is true?
A. The operating profit last month was $50,000, and the inventory value is $15,000.
B. The operating profit last month was $50,000, and the inventory value is $45,000.
C. The operating profit last month was $125,000, and the inventory value is $30,000.
D. The operating profit last month was $200,000, and the inventory value is $30,000.
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only IMANET exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your IMANET-CMA exam preparations and IMANET certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.