Exam Details
Exam Code
:PW0-250Exam Name
:Certified Wireless Design Professional (CWDP)Certification
:CWNP CertificationsVendor
:CWNPTotal Questions
:65 Q&AsLast Updated
:Aug 16, 2025
CWNP CWNP Certifications PW0-250 Questions & Answers
-
Question 21:
A wireless engineer from your company performed a site survey in an office building where a wireless network extension was needed. He reports that while performing a Layer 1 sweep near a meeting room full of people, he detected the RF environment displayed in the exhibit. He is unsure how to interpret what he recorded to determine its impact on a future Wi-Fi network.

A. The signal affects the entire spectrum and will render the wireless network unusable. It must be located and removed.
B. The signal has a low duty cycle and should not be of major impact on the wireless network.
C. The signal is alternating between peaks (high interference level) and valleys (low interference level). The network channel design must be built to avoid the affected peak frequencies.
D. The signal is typical of a high radio card background noise. It shows that the card used for the Layer 1 sweep should be replaced and the Layer 1 sweep re-done.
E. The Real Time FFT shows a high amplitude, narrowband jammer pulsing across the entire 2.4 GHz band. This will cause significant, intermittent interference to the WLAN.
-
Question 22:
You are on site, planning a network at a freight shipping company on a busy harbor. Since the preliminary WLAN design specifies support for the 5 GHz spectrum, you would like to test for radar pulses to determine if DFS channels should be supported at this facility. As a part of your spectral survey with a laptop-based analyzer, you include DFS testing to identify the presence of radar. This is done by manually observing Real-time FFT, Duty Cycle, and Active Devices charts of the spectrum analyzer software.
What potential drawback is present with this DFS test method? (Choose 3)
A. Many WLAN products that support DFS channels report several false positives. Ideally, the actual WLAN equipment used in the deployment should be used to test for DFS.
B. Some sources of 5 GHz radar, such as military ships, are mobile in nature. A longer, automated test setup should be used to identify the presence or absence of radar.
C. Manual identification of radar pulses using spectrum analysis charts can be very difficult due to radar's low amplitude at the Wi-Fi receiver.
D. Modern spectrum analyzer adapters do not provide the necessary bandwidth resolution required to detect and measure radar signatures.
-
Question 23:
When performing an indoor predictive site survey to make the WLAN planning and design cycle more efficient, what is a best practice for configuration of the simulated APs in the predictive modeling software?
A. All simulated APs should be set to 20 MHz channels only.
B. Always use the default 2.2 dBi omnidirectional antenna patterns for simulated APs.
C. If dynamic RRM will be used, AP transmit power should be set to an estimated average level of the expected client devices, such as 25 mW.
D. Defining custom AP and antenna patterns will yield more accurate prediction data than the pre- configured vendor AP/antenna combinations.
-
Question 24:
What exhibit reflects the recommended life-cycle steps for successfully designing and deploying an enterprise WLAN from start to finish? (Choose 2)

A. Solution 1
B. Solution 2
C. Solution 3
D. Solution 4
E. Solution 5
-
Question 25:
What is a valid 40 MHz channel configuration in the 2.4 GHz ISM band where channels 1-11 are permitted? (Choose 2)
A. 4 (primary), +1 (secondary)
B. 4 (primary), -1 (secondary)
C. 8 (primary), +1 (secondary)
D. 1 (primary), 6 (secondary)
E. 11 (primary), 6 (secondary)
F. 1 (primary), 5 (secondary)
-
Question 26:
Assume that your network operates in a regulatory domain that allows use of UNII-1, UNII-2, UNII- 2e, UNII-3, and the 5.8 GHz ISM band for indoor Wi-Fi. In your upcoming 802.11n deployment, you would like to take advantage of the performance improvements that result from channel bonding. However, after extensive testing, you have determined that your mission-critical WLAN should not use channels requiring DFS support.
Given those two criteria (enable channel bonding and disable DFS channels), in the 5 GHz spectrum, how many non-overlapping channels will your system be able to use?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 6
E. 11
-
Question 27:
Assuming an identical RF environment,

which one of these scenarios is most likely to lead to a client-to-AP link imbalance in which one- way communication results?
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 28:
Use the exhibit as a reference.
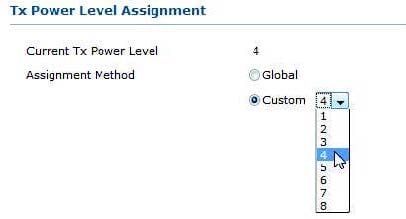
Given:
-In your regulatory domain, a Tx Power Level of "1" is equivalent to 17 dBm.
-For every integer increment (e.g. from 1 to 2) to the Tx Power Level, the AP's transmit power is halved.
In units of mW, what is the actual transmit power for an AP configured at a Tx Power Level of "4"?
A. 200 mW
B. 50 mW
C. 12.5 mW
D. 8 mW
E. 6.25 mW
F. 2.5 mW
-
Question 29:
You told your customer that multipath fading may be mitigated simply by moving one or both of the receiver's antennas a little bit, usually by one to four wavelengths away from its original position. Your customer is prepared to make the change, but does not know the wavelength for 802.11a.
What is the approximate wavelength of an 802.11a radio wave?
A. 5.5 cm (2.16 inches)
B. 12 cm (4.72 inches)
C. 15.24 cm (6 inches)
D. 45 cm (17.71 inches)
E. 58 cm (22.83 inches)
-
Question 30:
Given: You are evaluating the theoretical and real-world RF gain benefits of transmit and receive features introduced by 802.11n with MIMO. This exercise allows you to quantify the feature's value in a real-world environment.
What is the maximum theoretical signal gain of chip-based TxBF and MRC (as features) when compared to the same AP using only a single antenna for transmit and receive (effectively simulating a 1x1 chip)?
A. 2 Rx or Tx chains = 3 dBi gain 3 Rx or Tx chains = approx 5 dBi gain 4 Rx or Tx chains = 6 dBi gain
B. 2 Rx or Tx chains = 1 dBi gain 3 Rx or Tx chains = 2 dBi gain 4 Rx or Tx chains = 3 dBi gain
C. 2 Rx or Tx chains = 3 dBi gain 3 Rx or Tx chains = 6 dBi gain 4 Rx or Tx chains = 9 dBi gain
D. 2 Rx or Tx chains = approx 4-6.5 dBi gain 3 Rx or Tx chains = approx 7-10 dBi gain 4 Rx or Tx chains = approx 10-12 dBi gain
E. The theoretical gains offered by each additional radio are different for TxBF and MRC.
Related Exams:
CWAP-402
Certified Wireless Analysis ProfessionalCWAP-403
Certified Wireless Analysis ProfessionalCWAP-404
Certified Wireless Analysis ProfessionalCWDP-303
Certified Wireless Design ProfessionalCWDP-304
Certified Wireless Design ProfessionalCWDP-305
Certified Wireless Design ProfessionalCWISA-102
Certified Wireless IoT Solutions AdministratorCWNA-106
Certified Wireless Network AdministratorCWNA-107
Certified Wireless Network AdministratorCWNA-108
Certified Wireless Network Administrator
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only CWNP exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your PW0-250 exam preparations and CWNP certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.