Exam Details
Exam Code
:PW0-250Exam Name
:Certified Wireless Design Professional (CWDP)Certification
:CWNP CertificationsVendor
:CWNPTotal Questions
:65 Q&AsLast Updated
:Aug 16, 2025
CWNP CWNP Certifications PW0-250 Questions & Answers
-
Question 11:
Excessive uplink RTP frame retransmissions can result in . (Choose 3)
A. Deauthentication of the transmitter by the receiver
B. Lowering of the data transmission rate by the transmitting station
C. MOS scores in excess of 5
D. Head-of-Line blocking at the receiver
E. Shortened battery life of a transmitting station
F. Increased jitter in a VoWiFi connection
-
Question 12:
At a university, the WLAN has been successfully deployed for ubiquitous access for faculty, students, and guests. Many student computer labs are available throughout the campus with wired network connectivity, but there are also a few smaller lab areas and workstations where Ethernet cabling is not available. For student wireless use, the students must authenticate against RADIUS/Active Directory using PEAP. Also, the network administrators at this university would like administrative access to these workstations when they are not in use by students so that the administrators can manage group policies, update OS patches, and perform other routine software maintenance.
What deployment options are available and recommended for both student use and remote administration of these workstations? (Choose 2)
A. Due to the architecture of 802.1X port-based access control, it is not possible for a wireless- only computer to access network services required by network administrators in this scenario.
B. Machine authentication accounts should be enabled to provide persistent machine network connectivity when student users are not associated.
C. The WLAN infrastructure vendor is responsible for providing proprietary client connectivity options to facilitate device connectivity without user interaction.
D. These workstations should be Ethernet-connected to a wireless client bridge, which will maintain network connectivity independent of student connectivity status.
E. These stations should be deployed with dual WLAN adapters. One adapter would be used for consistent network connectivity for administrative purposes and the second adapter should be used for student access.
-
Question 13:
You are site surveying a network for VoWiFi. You have positioned an AP for a manual survey and are moving away from the AP with a phone in Survey Mode in your hand and you are reading the RSSI value of the signal received from the AP. You have previously determined that the noise floor was approximately -94 dBm on this floor of the building. The phone's documentation does not specify a recommended RSSI or SNR value for best performance. Based on the
information provided and the type of device (VoWiFi phone) you are deploying, what minimum RSSI should you plan for in all areas you are monitoring and where VoWiFi service is desired?
A. -75 dBm
B. -72 dBm
C. -67 dBm
D. -62 dBm
E. -58 dBm
-
Question 14:
What statement is true of a WLAN design that supports Real-Time Location Services (RTLS) with 802.11 RFID asset tags? (Choose 2)
A. When passive tags are implemented, the AP density should be increased by 25% to make up for the shorter transmit range of passive tags as compared to active tags.
B. Active RFID tags periodically transmit 802.11 beacon management frames that must be synchronized with the AP for proper location of the tagged asset.
C. With passive tags, AP transmit gain should be increased to supply extra power for near-field coupling or backscatter modulation from the tag to the AP since the passive tag lacks an internal power source.
D. Passive tags do not communicate directly with the WLAN infrastructure, but instead they rely on the tag interrogator to communicate tag information to the infrastructure's location tracking server/database.
E. Active tags transmit directly to the APs and may not require 802.11 authentication and association to pass data traffic to the RTLS engine.
F. When tracking assets with passive RFID tags, some APs should be moved, or additional APs be added, to provide more accurate triangulation and location services.
-
Question 15:
Given: In a site survey deliverable report, you are expected to explain the spectrum measurements taken at the customer's site. The exhibit shows a representative sample capture of the RF environment at one of the customer sites.

What best explains the data presented in this exhibit?
A. The Real Time FFT chart shows a high noise floor across the entire 2.4 GHz band.
B. Channel 1 is being heavily utilized by Wi-Fi and channel 11 also has some moderate Wi-Fi activity.
C. As indicated by the data in the Active Devices list, the spectrum analysis chipset is also reporting 802.11 information.
D. Although some access points are present in a nearby area, they are not being heavily used.
-
Question 16:
You are testing a VoWLAN deployment, and your communication measurements show a certain amount of lost packets. What would be an acceptable packet error rate value to still provide acceptable call quality?
A. There should be 0% error in a VoWLAN type of deployment
B. No more than 1% PER max should be acceptable
C. No more than 4% PER max should be acceptable
D. No more than 8% PER max should be acceptable
E. No more than 12% PER max should be acceptable
-
Question 17:
A Layer 1 sweep was performed at a customer location, and you are asked to review a capture taken during the survey.

What is the meaning of the chart shown in the exhibit and how should it be interpreted?
A. Real Time FFT means Real Time First Fundamental Trace and shows the value of the first signal detected on each frequency at each sweep interval.
B. Real Time FFT means Real Time Fast Frequency Timing and shows the RF pulses measured by the Layer 1 sweep tool.
C. Real Time FFT means Real Time Fast Fourier Transform and shows the max value of the signal detected on each frequency in real time.
D. Real Time FFT means Real Time Frequency Fundamental Texture and shows the value of the noise background generated by the card used to perform the Layer 1 sweep.
-
Question 18:
In a PC-based spectrum analyzer, what data chart identifies the overall RF utilization of a specific frequency in the environment being surveyed?
A. FFT Max Hold
B. FFT Average
C. Swept Spectrogram
D. Duty cycle
E. Sweep Time
F. Bandwidth resolution
-
Question 19:
When preparing a floor plan graphic for use in predictive and manual site surveying, what calibration method will lead to the most accurate and reliable RF data?
A. Use the known size of a small object, such as a ceiling tile, and use a single instance of this object (e.g. a single ceiling tile) to scale the floor plan.
B. Measure the width of an actual office doorway with a tape measure and use this value to calibrate against a doorway graphic.
C. Use the longest available measurement (like a straight exterior wall) to calibrate the graphic's scale.
D. Calibrate the ceiling height of the floor plan first, then the survey software should be able to auto-calibrate the X and Y planes of the graphic.
E. With properly formatted .bmp and .png graphics, the site survey software should be able to extract the scale directly from the graphic data during import.
-
Question 20:
While configuring your site survey software for an upcoming manual survey project, you notice the configuration option for "Network Card Simu-lation" as shown in the exhibit.
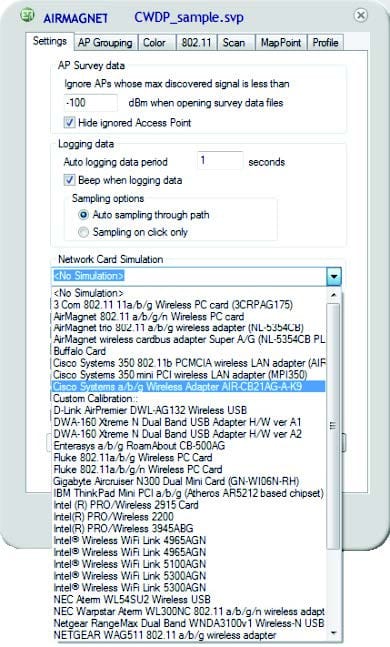
A. This setting allows the site survey software to convert the AP's measured downlink RF data into a simulated data set as if the same data were transmitted by a specific client station. It is useful for determining uplink client performance when clients are located far from APs as well as projecting cell size for ad hoc networks.
B. Since WLAN adapters are not typically calibrated by manufacturers, this setting is a form of software calibration in which you can calibrate an (uncalibrated) adapter to match one of thecalibrated adapters shown in the list. This process improves the reliability of RF data collection and reporting when uncalibrated adapters are used.
C. This is the configuration area in which you specify the adapter type that will be used for the site survey so that the survey software can interpret that adapter's reported metrics (based on proprietary formulas) into an RF measurement that is standardized by the survey software and known to its users. This is done for every survey.
D. The site survey software manufacturer allows you to view the collected RF data as if it were collected by a different type of adapter. This functionality allows you to review survey data to determine how the RF environment will likely look based on the receive sensitivity and other RF capabilities of a specific client adapter.
Related Exams:
CWAP-402
Certified Wireless Analysis ProfessionalCWAP-403
Certified Wireless Analysis ProfessionalCWAP-404
Certified Wireless Analysis ProfessionalCWDP-303
Certified Wireless Design ProfessionalCWDP-304
Certified Wireless Design ProfessionalCWDP-305
Certified Wireless Design ProfessionalCWISA-102
Certified Wireless IoT Solutions AdministratorCWNA-106
Certified Wireless Network AdministratorCWNA-107
Certified Wireless Network AdministratorCWNA-108
Certified Wireless Network Administrator
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only CWNP exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your PW0-250 exam preparations and CWNP certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.