Exam Details
Exam Code
:SAP-C01Exam Name
:AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Professional (SAP-C01)Certification
:Amazon CertificationsVendor
:AmazonTotal Questions
:973 Q&AsLast Updated
:Jul 09, 2023
Amazon Amazon Certifications SAP-C01 Questions & Answers
-
Question 401:
A Solutions Architect is responsible for redesigning a legacy Java application to improve its availability, data durability, and scalability. Currently, the application runs on a single high-memory Amazon EC2 instance. It accepts HTTP requests from upstream clients, adds them to an in-memory queue, and responds with a 200 status. A separate application thread reads items from the queue, processes them, and persists the results to an Amazon RDS MySQL instance. The processing time for each item takes 90 seconds on average, most of which is spent waiting on external service calls, but the application is written to process multiple items in parallel.
Traffic to this service is unpredictable. During periods of high load, items may sit in the internal queue for over an hour while the application processes the backlog. In addition, the current system has issues with availability and data loss if the single application node fails.
Clients that access this service cannot be modified. They expect to receive a response to each HTTP request they send within 10 seconds before they will time out and retry the request.
Which approach would improve the availability and durability of the system while decreasing the processing latency and minimizing costs?
A. Create an Amazon API Gateway REST API that uses Lambda proxy integration to pass requests to an AWS Lambda function. Migrate the core processing code to a Lambda function and write a wrapper class that provides a handler method that converts the proxy events to the internal application data model and invokes the processing module.
B. Create an Amazon API Gateway REST API that uses a service proxy to put items in an Amazon SQS queue. Extract the core processing code from the existing application and update it to pull items from Amazon SQS instead of an in- memory queue. Deploy the new processing application to smaller EC2 instances within an Auto Scaling group that scales dynamically based on the approximate number of messages in the Amazon SQS queue.
C. Modify the application to use Amazon DynamoDB instead of Amazon RDS. Configure Auto Scaling for the DynamoDB table. Deploy the application within an Auto Scaling group with a scaling policy based on CPU utilization. Back the in- memory queue with a memory-mapped file to an instance store volume and periodically write that file to Amazon S3.
D. Update the application to use a Redis task queue instead of the in-memory queue. Build a Docker container image for the application. Create an Amazon ECS task definition that includes the application container and a separate container to host Redis. Deploy the new task definition as an ECS service using AWS Fargate, and enable Auto Scaling.
-
Question 402:
A company wants to allow its Marketing team to perform SQL queries on customer records to identify market segments. The data is spread across hundreds of files. The records must be encrypted in transit and at rest. The Team Manager must have the ability to manage users and groups, but no team members should have access to services or resources not required for the SQL queries. Additionally, Administrators need to audit the queries made and receive notifications when a query violates rules defined by the Security team.
AWS Organizations has been used to create a new account and an AWS IAM user with administrator permissions for the Team Manager.
Which design meets these requirements?
A. Apply a service control policy (SCP) that allows access to IAM, Amazon RDS, and AWS CloudTrail. Load customer records in Amazon RDS MySQL and train users to execute queries using the AWS CLI. Stream the query logs to Amazon CloudWatch Logs from the RDS database instance. Use a subscription filter with AWS Lambda functions to audit and alarm on queries against personal data.
B. Apply a service control policy (SCP) that denies access to all services except IAM, Amazon Athena, Amazon S3, and AWS CloudTrail. Store customer record files in Amazon S3 and train users to execute queries using the CLI via Athena. Analyze CloudTrail events to audit and alarm on queries against personal data.
C. Apply a service control policy (SCP) that denies access to all services except IAM, Amazon DynamoDB, and AWS CloudTrail. Store customer records in DynamoDB and train users to execute queries using the AWS CLI. Enable DynamoDB streams to track the queries that are issued and use an AWS Lambda function for real-time monitoring and alerting.
D. Apply a service control policy (SCP) that allows access to IAM, Amazon Athena, Amazon S3, and AWS CloudTrail. Store customer records as files in Amazon S3 and train users to leverage the Amazon S3 Select feature and execute queries using the AWS CLI. Enable S3 object-level logging and analyze CloudTrail events to audit and alarm on queries against personal data.
-
Question 403:
A company has a 24 TB MySQL database in its on-premises data center that grows at the rate of 10 GB per day. The data center is connected to the company's AWS infrastructure with a 50 Mbps VPN connection.
The company is migrating the application and workload to AWS. The application code is already installed and tested on Amazon EC2. The company now needs to migrate the database and wants to go live on AWS within 3 weeks.
Which of the following approaches meets the schedule with LEAST downtime?
A. 1. Use the VM Import/Export service to import a snapshot of the on-premises database into AWS.
2.
Launch a new EC2 instance from the snapshot.
3.
Set up ongoing database replication from on premises to the EC2 database over the VPN.
4.
Change the DNS entry to point to the EC2 database.
5.
Stop the replication.
B. 1. Launch an AWS DMS instance.
2.
Launch an Amazon RDS Aurora MySQL DB instance.
3.
Configure the AWS DMS instance with on-premises and Amazon RDS database information.
4.
Start the replication task within AWS DMS over the VPN.
5.
Change the DNS entry to point to the Amazon RDS MySQL database.
6.
Stop the replication.
C. 1. Create a database export locally using database-native tools.
2.
Import that into AWS using AWS Snowball.
3.
Launch an Amazon RDS Aurora DB instance.
4.
Load the data in the RDS Aurora DB instance from the export.
5.
Set up database replication from the on-premises database to the RDS Aurora DB instance over the VPN.
6.
Change the DNS entry to point to the RDS Aurora DB instance.
7.
Stop the replication.
D. 1. Take the on-premises application offline.
2.
Create a database export locally using database-native tools.
3.
Import that into AWS using AWS Snowball.
4.
Launch an Amazon RDS Aurora DB instance.
5.
Load the data in the RDS Aurora DB instance from the export.
6.
Change the DNS entry to point to the Amazon RDS Aurora DB instance.
7.
Put the Amazon EC2 hosted application online.
-
Question 404:
A company is creating an account strategy so that they can begin using AWS. The Security team will provide each team with the permissions they need to follow the principle or least privileged access. Teams would like to keep their resources isolated from other groups, and the Finance team would like each team's resource usage separated for billing purposes.
Which account creation process meets these requirements and allows for changes?
A. Create a new AWS Organizations account. Create groups in Active Directory and assign them to roles in AWS to grant federated access. Require each team to tag their resources, and separate bills based on tags. Control access to resources through IAM granting the minimally required privilege.
B. Create individual accounts for each team. Assign the security account as the master account, and enable consolidated billing for all other accounts. Create a cross-account role for security to manage accounts, and send logs to a bucket in the security account.
C. Create a new AWS account, and use AWS Service Catalog to provide teams with the required resources. Implement a third-party billing solution to provide the Finance team with the resource use for each team based on tagging. Isolate resources using IAM to avoid account sprawl. Security will control and monitor logs and permissions.
D. Create a master account for billing using Organizations, and create each team's account from that master account. Create a security account for logs and cross-account access. Apply service control policies on each account, and grant the Security team cross-account access to all accounts. Security will create IAM policies for each account to maintain least privilege access.
-
Question 405:
A company wants to launch an online shopping website in multiple countries and must ensure that customers are protected against potential "man-in-the-middle" attacks.
Which architecture will provide the MOST secure site access?
A. Use Amazon Route 53 for domain registration and DNS services. Enable DNSSEC for all Route 53 requests. Use AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) to register TLS/SSL certificates for the shopping website, and use Application Load Balancers configured with those TLS/SSL certificates for the site. Use the Server Name Identification extension in all client requests to the site.
B. Register 2048-bit encryption keys from a third-party certificate service. Use a third-party DNS provider that uses the customer managed keys for DNSSec. Upload the keys to ACM, and use ACM to automatically deploy the certificates for secure web services to an EC2 front-end web server fleet by using NGINX. Use the Server Name Identification extension in all client requests to the site.
C. Use Route 53 for domain registration. Register 2048-bit encryption keys from a third-party certificate service. Use a third-party DNS service that supports DNSSEC for DNS requests that use the customer managed keys. Import the customer managed keys to ACM to deploy the certificates to Classic Load Balancers configured with those TLS/SSL certificates for the site. Use the Server Name Identification extension in all clients requests to the site.
D. Use Route 53 for domain registration, and host the company DNS root servers on Amazon EC2 instances running Bind. Enable DNSSEC for DNS requests. Use ACM to register TLS/SSL certificates for the shopping website, and use Application Load Balancers configured with those TLS/SSL certificates for the site. Use the Server Name Identification extension in all client requests to the site.
-
Question 406:
A retail company is running an application that stores invoice files in an Amazon S3 bucket and metadata about the files in an Amazon DynamoDB table. The application software runs in both us-east-1 and euwest-1. The S3 bucket and DynamoDB table are in us-east-1. The company wants to protect itself from data corruption and loss of connectivity to either Region.
Which option meets these requirements?
A. Create a DynamoDB global table to replicate data between us-east-1 and eu-west-1. Enable continuous backup on the DynamoDB table in us-east-1. Enable versioning on the S3 bucket.
B. Create an AWS Lambda function triggered by Amazon CloudWatch Events to make regular backups of the DynamoDB table. Set up S3 cross-region replication from us-east-1 to eu-west-1. Set up MFA delete on the S3 bucket in us-east- 1.
C. Create a DynamoDB global table to replicate data between us-east-1 and eu-west-1. Enable versioning on the S3 bucket. Implement strict ACLs on the S3 bucket.
D. Create a DynamoDB global table to replicate data between us-east-1 and eu-west-1. Enable continuous backup on the DynamoDB table in us-east-1. Set up S3 cross-region replication from useast-1 to eu-west-1.
-
Question 407:
A company is designing a new highly available web application on AWS. The application requires consistent and reliable connectivity from the application servers in AWS to a backend REST API hosted in the company's on-premises environment. The backend connection between AWS and on-premises will be routed over an AWS Direct Connect connection through a private virtual interface. Amazon Route 53 will be used to manage private DNS records for the application to resolve the IP address on the backend REST API.
Which design would provide a reliable connection to the backend API?
A. Implement at least two backend endpoints for the backend REST API, and use Route 53 health checks to monitor the availability of each backend endpoint and perform DNS-level failover.
B. Install a second Direct Connect connection from a different network carrier and attach it to the same virtual private gateway as the first Direct Connect connection.
C. Install a second cross connect for the same Direct Connect connection from the same network carrier, and join both connections to the same link aggregation group (LAG) on the same private virtual interface.
D. Create an IPSec VPN connection routed over the public internet from the on-premises data center to AWS and attach it to the same virtual private gateway as the Direct Connect connection.
-
Question 408:
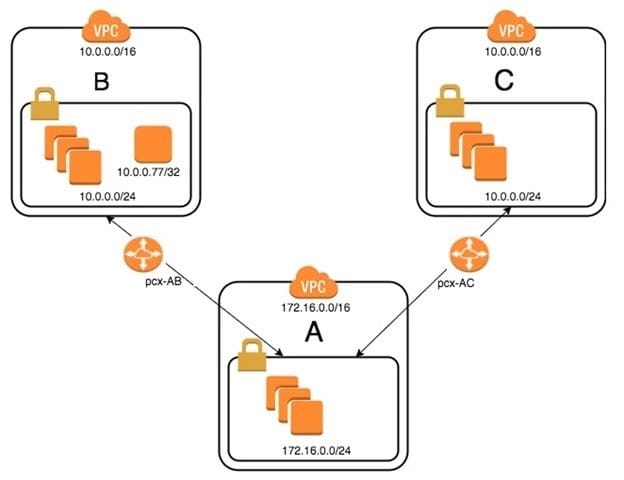
An organization has recently grown through acquisitions. Two of the purchased companies use the same IP CIDR range. There is a new short-term requirement to allow AnyCompany A (VPC-A) to communicate with a server that has the IP address 10.0.0.77 in AnyCompany B (VPC-B). AnyCompany A must also communicate with all resources in AnyCompany C (VPC-C). The Network team has created the VPC peer links, but it is having issues with communications between VPC-A and VPC-B. After an investigation, the team believes that the routing tables in the VPCs are incorrect.
What configuration will allow AnyCompany A to communicate with AnyCompany C in addition to the database in AnyCompany B?
A. On VPC-A, create a static route for the VPC-B CIDR range (10.0.0.0/24) across VPC peer pcx-AB. Create a static route of 10.0.0.0/16 across VPC peer pcx-AC.
On VPC-B, create a static route for VPC-A CIDR (172.16.0.0/24) on peer pcx-AB.
On VPC-C, create a static route for VPC-A CIDR (172.16.0.0/24) across peer pcx-AC.
B. On VPC-A, enable dynamic route propagation on pcx-AB and pcx-AC. On VPC-B, enable dynamic route propagation and use security groups to allow only the IP address 10.0.0.77/32 on VPC peer pcx-AB. On VPC-C, enable dynamic route propagation with VPC-A on peer pcx-AC.
C. On VPC-A, create network access control lists that block the IP address 10.0.0.77/32 on VPC peer pcx-AC. On VPC-A, create a static route for VPC-B CIDR (10.0.0.0/24) on pcx-AB and a static route for VPC-C CIDR (10.0.0.0/24) on pcx-AC. On VPC-B, create a static route for VPC-A CIDR (172.16.0.0/24) on peer pcx-AB. On VPC-C, create a static route for VPC-A CIDR (172.16.0.0/24) across peer pcx-AC.
D. On VPC-A, create a static route for the VPC-B (10.0.0.77/32) database across VPC peer pcx-AB. Create a static route for the VPC-C CIDR on VPC peer pcx-AC. On VPC-B, create a static route for VPC-A CIDR (172.16.0.0/24) on peer pcx-AB. On VPC-C, create a static route for VPC-A CIDR (172.16.0.0/24) across peer pcx-AC.
-
Question 409:
A company runs an ordering system on AWS using Amazon SQS and AWS Lambda, with each order received as a JSON message. Recently the company had a marketing event that led to a tenfold increase in orders. With this increase, the following undesired behaviors started in the ordering system:
1.
Lambda failures while processing orders lead to queue backlogs.
2.
The same orders have been processed multiple times.
A Solutions Architect has been asked to solve the existing issues with the ordering system and add the following resiliency features:
1.
Retain problematic orders for analysis.
2.
Send notification if errors go beyond a threshold value.
How should the Solutions Architect meet these requirements?
A. Receive multiple messages with each Lambda invocation, add error handling to message processing code and delete messages after processing, increase the visibility timeout for the messages, create a dead letter queue for messages that could not be processed, create an Amazon CloudWatch alarm on Lambda errors for notification.
B. Receive single messages with each Lambda invocation, put additional Lambda workers to poll the queue, delete messages after processing, increase the message timer for the messages, use Amazon CloudWatch Logs for messages that could not be processed, create a CloudWatch alarm on Lambda errors for notification.
C. Receive multiple messages with each Lambda invocation, use long polling when receiving the messages, log the errors from the message processing code using Amazon CloudWatch Logs, create a dead letter queue with AWS Lambda to capture failed invocations, create CloudWatch events on Lambda errors for notification.
D. Receive multiple messages with each Lambda invocation, add error handling to message processing code and delete messages after processing, increase the visibility timeout for the messages, create a delay queue for messages that could not be processed, create an Amazon CloudWatch metric on Lambda errors for notification.
-
Question 410:
A company is currently using AWS CodeCommit for its source control and AWS CodePipeline for continuous integration. The pipeline has a build stage for building the artifacts, which is then staged in an Amazon S3 bucket.
The company has identified various improvement opportunities in the existing process, and a Solutions Architect has been given the following requirements:
1.
Create a new pipeline to support feature development
2.
Support feature development without impacting production applications
3.
Incorporate continuous testing with unit tests
4.
Isolate development and production artifacts
5.
Support the capability to merge tested code into production code.
How should the Solutions Architect achieve these requirements?
A. Trigger a separate pipeline from CodeCommit feature branches. Use AWS CodeBuild for running unit tests. Use CodeBuild to stage the artifacts within an S3 bucket in a separate testing account.
B. Trigger a separate pipeline from CodeCommit feature branches. Use AWS Lambda for running unit tests. Use AWS CodeDeploy to stage the artifacts within an S3 bucket in a separate testing account.
C. Trigger a separate pipeline from CodeCommit tags. Use Jenkins for running unit tests. Create a stage in the pipeline with S3 as the target for staging the artifacts with an S3 bucket in a separate testing account.
D. Create a separate CodeCommit repository for feature development and use it to trigger the pipeline. Use AWS Lambda for running unit tests. Use AWS CodeBuild to stage the artifacts within different S3 buckets in the same production account.
Related Exams:
AIF-C01
Amazon AWS Certified AI Practitioner (AIF-C01)ANS-C00
AWS Certified Advanced Networking - Specialty (ANS-C00)ANS-C01
AWS Certified Advanced Networking - Specialty (ANS-C01)AXS-C01
AWS Certified Alexa Skill Builder - Specialty (AXS-C01)BDS-C00
AWS Certified Big Data - Speciality (BDS-C00)CLF-C02
AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner (CLF-C02)DAS-C01
AWS Certified Data Analytics - Specialty (DAS-C01)DATA-ENGINEER-ASSOCIATE
AWS Certified Data Engineer - Associate (DEA-C01)DBS-C01
AWS Certified Database - Specialty (DBS-C01)DOP-C02
AWS Certified DevOps Engineer - Professional (DOP-C02)
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Amazon exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your SAP-C01 exam preparations and Amazon certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.