Exam Details
Exam Code
:JN0-343Exam Name
:Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT)Certification
:Juniper CertificationsVendor
:JuniperTotal Questions
:563 Q&AsLast Updated
:
Juniper Juniper Certifications JN0-343 Questions & Answers
-
Question 281:
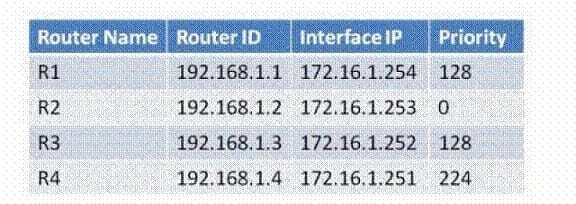
In the exhibit, four routers (R1, R2, R3, and R4) are attached to a single Ethernet LAN and configured with addresses in the same subnet. All devices boot at the same time. Which router or routers will send a Network (Type 2) LSA for the network?
A. R2
B. R4
C. R1 and R2
D. R3 and R4
-
Question 282:
You want STP to behave similar to RSTP.
Which three configuration settings under the [edit protocols stp] hierarchy on an EX Series switch allow this? (Choose three.)
A. max-age
B. bridge-priority
C. edge
D. forwarding-delay
E. hello-time
-
Question 283:
What is the default next-hop behavior for aggregate routes?
A. discard
B. resolve
C. reject
D. direct
-
Question 284:
You have a traditional 3-tier network design.
What are two functions of the aggregation layer? (Choose two.)
A. It functions as the gateway to the WAN edge.
B. It connects access layer switches.
C. It provides inter-VLAN routing.
D. It facilitates device access.
-
Question 285:
Why does a router create an ASBRSum (Type 4) LSA?
A. An ABR creates an ASBRSum (Type 4) LSA with the information contained in NSSA (Type 7) LSAs it receives from NSSAs.
B. An ABR creates an ASBRSum (Type 4) LSA to describe the router ID of ASBRs located in other areas.
C. An ASBR creates an ASBRSum (Type 4) LSA to describe its router ID so that routers in other areas can reach the external networks it advertises.
D. An ABR creates an ASBRSum (Type 4) LSA to summarize routes received from other areas.
-
Question 286:
ON NO: 207
What is preserved by enabling graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES)?
A. control-plane state
B. link-state protocol adjacencies
C. interface and kernel information
D. BGP peering relationships
-
Question 287:
You want to configure a redundant trunk group on a switch. You want ge-0/0/0.0 to be the default link; however, if ge-0/0/0.0 fails and the switch begins using ge-0/0/1.0, you want the switch to continue using ge-0/0/1.0 until ge-0/0/1.0 fails. Which configuration will accomplish this scenario?
A. redundant-trunk-group { interface ge-0/0/0.0 { primary; } interface ge-0/0/1.0 { primary; } }
B. redundant-trunk-group { interface ge-0/0/0.0; interface ge-0/0/1.0; no-preempt; }
C. redundant-trunk-group { interface ge-0/0/0.0 { primary; } interface ge-0/0/1.0; }
D. redundant-trunk-group { interface ge-0/0/0.0; interface ge-0/0/1.0; }
-
Question 288:
Which two statements are true of IS-IS? (Choose two.)
A. When configured on a broadcast segment, IS-IS elects a designated intermediate system that establishes adjacencies with all IS-IS enabled nodes on the segment.
B. When configured on a broadcast segment, IS-IS forms a full mesh of adjacencies called a mesh group; unlike OSPF, no designated device exists to represent the segment.
C. When configured on a broadcast segment, IS-IS elects a backup designated intermediate system.
D. When configured on a broadcast segment, the network itself is called a pseudo-node
-
Question 289:
You want to ensure that all traffic arriving on interface fe-0/0/0.0 will be routed to next-hop 10.1.1.1, regardless of the more specific routes that might appear in the routing table. How can you accomplish this configuration?
A. Configure a default route with a next hop of 10.1.1.1 and configure the always-use flag for the route.
B. Configure and apply a firewall filter that sends all traffic to a routing instance, configure a default route in that routing instance, and configure the router to install interface routes in that routing instance.
C. Configure a routing policy that matches all traffic and sets the next hop to 10.1.1.1, and configure a RIB group to ensure that the routing policy can resolve the next hop to 10.1.1.1.
D. Configure a firewall filter that matches all traffic and sets the next hop to 10.1.1.1, apply the firewall filter to a RIB group, and assign the fe-0/0/0.0 interface to that RIB group.
-
Question 290:

In the exhibit, six routers (R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, and R6) are attached to a single Ethernet
LAN and configured with addresses in the same subnet. All devices boot at the same time. Which router will become the designated router (DR), and which router will become the backup designated router (BDR)?
A. DR:R3 BDR: R4
B. DR: R4 BDR: R3
C. DR: R6 BDR: R1
D. DR: R6 BDR: R2
Related Exams:
JN0-102
Internet Associate, Junos(JNCIA-Junos)JN0-104
Junos, Associate (JNCIA-Junos)JN0-105
Junos, Associate (JNCIA-Junos)JN0-1101
Juniper Networks Certified Design Associate (JNCDA)JN0-1103
Design, Associate (JNCIA-Design)JN0-130
Juniper networks Certified internet specialist.e(jncis-e)JN0-1301
Data Center Design, Specialist (JNCDS-DC)JN0-1302
Data Center Design Specialist (JNCDS-DC)JN0-1331
Security Design, Specialist (JNCDS-SEC)JN0-1332
Security Design, Specialist (JNCDS-SEC)
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Juniper exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your JN0-343 exam preparations and Juniper certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.