Exam Details
Exam Code
:JN0-332Exam Name
:Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist, SEC (JNCIS-SEC)Certification
:Juniper CertificationsVendor
:JuniperTotal Questions
:519 Q&AsLast Updated
:Jun 06, 2025
Juniper Juniper Certifications JN0-332 Questions & Answers
-
Question 281:
Click the Exhibit button.
user@host> show interfaces ge-0/0/0.0 | match host-inbound Allowed host-inbound traffic : ping ssh telnet
Which configuration would result in the output shown in the exhibit?
A. [edit security zones security-zone trust] user@host# show host-inbound-traffic { system-services { ping; telnet; }} interfaces { ge-0/0/0.0 { host-inbound-traffic { system-services { ssh; telnet; }}}}
B. [edit security zones functional-zone management] user@host# show interfaces { all; } host-inbound-traffic { system-services { all;
ftp {
except;
}}}
C. [edit security zones functional-zone management] user@host# show interfaces { all { host-inbound-traffic { system-services { ping; }}}} host-inbound-traffic { system-services { telnet; ssh; }}
D. [edit security zones security-zone trust] user@host# show host-inbound-traffic { system-services { ssh; ping; telnet; }} interfaces { ge-0/0/3.0 { host-inbound-traffic { system-services { ping; }}} ge-0/0/0.0; }
-
Question 282:
Click the Exhibit button.
user@host> show interfaces ge-0/0/0.0 | match host-inbound Allowed host-inbound traffic : bgp ospf
Which configuration would result in the output shown in the exhibit?
A. [edit security zones functional-zone management] user@host# show interfaces { ge-0/0/0.0 { host-inbound-traffic { protocols { bgp; ospf; vrrp; }}}} host-inbound-traffic { protocols { all; vrrp { except;
}}}
B. [edit security zones functional-zone management] user@host# show host-inbound-traffic { protocols { bgp; ospf; }}
C. [edit security zones security-zone trust] user@host# show interfaces { ge-0/0/0.0 { host-inbound-traffic { protocols { ospf; bgp; }}}}
D. [edit security zones security-zone trust] user@host# show host-inbound-traffic { protocols { bgp; }} interfaces { all { host-inbound-traffic { protocols { ospf; }}}}
-
Question 283:
Click the Exhibit button.
[edit security zones security-zone HR]
user@host# show
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ping;
ssh;
https;
}}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/0.0;
ge-0/0/1.0 {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ping;
}}}
ge-0/0/2.0 {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ping;
ftp;
}}}
ge-0/0/3.0 {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
all;
ssh {
except;
}}}
}}
All system services have been enabled.
Given the configuration shown in the exhibit, which interface allows both ping and SSH traffic?
A. ge-0/0/0.0
B. ge-0/0/1.0
C. ge-0/0/2.0
D. ge-0/0/3.0
-
Question 284:
Click the Exhibit button.
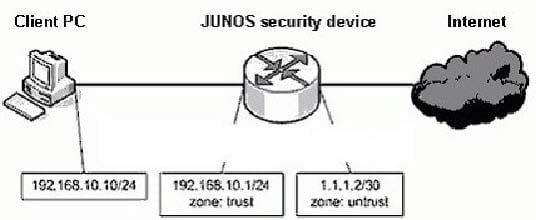
Based on the exhibit, client PC 192.168.10.10 cannot ping 1.1.1.2. Which is a potential cause for this problem?
A. The untrust zone does not have a management policy configured.
B. The trust zone does not have ping enabled as a host-inbound-traffic service.
C. The security policy from the trust zone to the untrust zone does not permit ping.
D. No security policy exists for the ICMP reply packet from the untrust zone to the trust zone.
-
Question 285:
Click the Exhibit button.
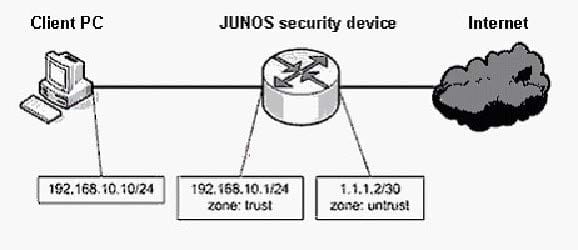
Referring to the exhibit, you are not able to telnet to 192.168.10.1 from client PC 192.168.10.10. What is causing the problem?
A. Telnet is not being permitted by self policy.
B. Telnet is not being permitted by security policy.
C. Telnet is not allowed because it is not considered secure.
D. Telnet is not enabled as a host-inbound service on the zone.
-
Question 286:
You are not able to telnet to the interface IP address of your device from a PC on the same subnet. What is causing the problem?
A. Telnet is not being permitted by self policy.
B. Telnet is not being permitted by security policy.
C. Telnet is not allowed because it is not considered secure.
D. Telnet is not enabled as a host-inbound service on the zone.
-
Question 287:
You want to create an out-of-band management zone and assign the ge-0/0/0.0 interface to that zone. From the [edit] hierarchy, which command do you use to configure this assignment?
A. set security zones management interfaces ge-0/0/0.0
B. set zones functional-zone management interfaces ge-0/0/0.0
C. set security zones functional-zone management interfaces ge-0/0/0.0
D. set security zones functional-zone out-of-band interfaces ge-0/0/0.0
-
Question 288:
You want to allow all hosts on interface ge-0/0/0.0 to be able to ping the device's ge- 0/0/0.0 IP address. Where do you configure this functionality?
A. [edit interfaces]
B. [edit security zones]
C. [edit system services]
D. [edit security interfaces]
-
Question 289:
Which two steps are performed when configuring a zone? (Choose two.)
A. Define a default policy for the zone.
B. Assign logical interfaces to the zone.
C. Assign physical interfaces to the zone.
D. Define the zone as a security or functional zone.
-
Question 290:
Which type of zone is used by traffic transiting the device?
A. transit zone
B. default zone
C. security zone
D. functional zone
Related Exams:
JN0-102
Internet Associate, Junos(JNCIA-Junos)JN0-104
Junos, Associate (JNCIA-Junos)JN0-105
Junos, Associate (JNCIA-Junos)JN0-1101
Juniper Networks Certified Design Associate (JNCDA)JN0-1103
Design, Associate (JNCIA-Design)JN0-130
Juniper networks Certified internet specialist.e(jncis-e)JN0-1301
Data Center Design, Specialist (JNCDS-DC)JN0-1302
Data Center Design Specialist (JNCDS-DC)JN0-1331
Security Design, Specialist (JNCDS-SEC)JN0-1332
Security Design, Specialist (JNCDS-SEC)
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Juniper exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your JN0-332 exam preparations and Juniper certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.