1Z0-997-22 Exam Details
-
Exam Code
:1Z0-997-22 -
Exam Name
:Oracle Cloud Infrastructure 2022 Architect Professional -
Certification
:Oracle Certifications -
Vendor
:Oracle -
Total Questions
:165 Q&As -
Last Updated
:Jan 17, 2026
Oracle 1Z0-997-22 Online Questions & Answers
-
Question 1:
You are a solution architect working with a startup that has decided to move their workload to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. Since their workload is small, upon architecting, you decide its sufficient to use 8 compute instances to run their workload. The company wants to use a common storage for their instances. So, you propose the idea of attaching a block volume to multiple instances to provide a common storage.
Which of the below option is NOT true for such a solution?
A. If the block volume is already attached to an instance as read/write non-shareable you can't attach it to another instance until you detach it from the first instance.
B. Block volumes attached as read-only are configured as shareable by default.
C. You can delete a block volume from one instance without detaching it from all other instances there by keeping other instance's storage intact.
D. Once you attach a block volume to an instance as read-only, it can only be attached to other instances as read-only. -
Question 2:
You have provisioned a new VM.DenseIO2.24 compute instance with local NVMe drives. The compute instance is running production application. This is a write heavy application, with a significant Impact to the business it the application goes down.
What should you do to help maintain write performance and protect against NVMe devices failure.
A. NVMe drive have built in capability to recover themself so no other actions are required
B. Configure RAID 6 for NVMe devices.
C. Configure RAID 1 for NVMe devices.
D. Configure RAID 10 for NVMe devices. -
Question 3:
Which of the following is NOT a good use case for the volume backup feature of the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Block Volume service?
A. Support business continuity requirements of reducing the risk of outages or data mutation over time.
B. Meet compliance and regulatory requirements for data to remain unchanged over time, so that it can be retrieved for audit purposes.
C. Rapidly duplicate an environment in seconds to test configuration changes without impacting your production environment.
D. Retain a copy of data in a volume, so that you can duplicate an environment later or preserve the data for future use. -
Question 4:
You are working with a customer who needs to attach an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) block volume to a VM instance with read/write access type. The customer wants to know if the number of IOPS and throughput performance differs between the following two choices:
Option A: attach a single 1 TB block volume to the VM instance Option B: attach two separate 500 GB block volumes In a RAID 0 array configuration to the VM instance
You can assume that the customer is using iSCSI attachment type to attach the volumes to the instance. In addition, you can assume 1 MB block size for throughput and 4 KB block size for IOPS consideration.
How should you respond to the customer?
A. Option B provides higher level of throughput, but lower level of IOPS performance.
B. Both options provide the same number of IOPS and throughput performance.
C. Option A provides better IOPS, but lower throughput performance.
D. Option B provides better IOPS and throughput performance. -
Question 5:
You have deployed a web application targeting a global audience across multiple Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) regions.
You decide to use Traffic Management Geo-Location based Steering Policy to serve web requests to users from the region closets to the user. Within each region you have deployed a public load balancer with 4 servers in a backend set. During a DR test disable all web servers in one of the regions however, traffic Management does not automatically direct all users to the other region.
Which two are possible causes?
A. You did not setup a Route Table associated with load Balancer's subnet
B. You did not setup an HTTP Health Check associated with Load Balancer public IP in the disabled region.
C. Rather than using Geo-Location based Steering Policy, you should use Failover Policy Type to serve traffic.
D. One of the two working web servers In the other region did not pass Its HTTP health check
E. You did not correctly setup the Load Balancer HTTP health check policy associated with backend set -
Question 6:
A hospital in Austin has hosted its web based medical records portal entirely In Oracle cloud Infrastructure (OCI) using Compute Instances for its web-tier and DB system database for its data tier. To validate compliance with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability (HIPAA), the security professional to check their systems it was found that there are a lot of unauthorized coming requests coming from a set of IP addresses originating from a country in Southeast Asia.
Which option can mitigate this type of attack?
A. Block the attacking IP address by creating by Network Security Group rule to deny access to the compute Instance where the web server Is running
B. Block the attacking IP address by implementing a OCI Web Application Firewall policy using Access Control Rules
C. Mitigate the attack by changing the Route fable to redirect the unauthorized traffic to a dummy Compute instance
D. Block the attacking IP address by creating a Security List rule to deny access to the subnet where the web server Is running -
Question 7:
Your organization is planning on using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) File Storage Service (FSS). You will be deploying multiple compute instance in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure(OCI) and mounting the file system to these compute instances.
The file system will hold payment data processed by a Database instance and utilized by compute instances to create a overall inventory report. You need to restrict access to this data for specific compute instances and must be allowed/ blocked per compute instance's CIDR block.
Which option can you use to secure access?
A. Create a new VCN security list, choose SOURCE TYPE as Service and SOURCE SERVICE as FSS. Add stateless ingress and egress rules for specific IP address and CIDR blocks.
B. Use 'Export option' feature of FSS to restrict access to the mounted file systems.
C. Create and configure OCI Web Application Firewall service with built in DNS based intelligent routing.
D. Use stateless Security List rule to restrict access from known IP addresses only. -
Question 8:
Your organization needs to migrate legacy monolithic applications into cloud-native containerized RESTful microservices. The development team is testing the use of packaged procedures with containers in a fully serverless environment. Before migrating the existing code to production, the team decides to perform a lift and shift of the monolithic application and code the new features that are essential for serverless microservices.
You want to carry out a steady migration to the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) platform, making the new microservice functionalities available while maintaining the monolithic application for all the other activities. You also want to integrate the legacy monolithic application with the new microservices to have a single interface with simplified management for auditing and monitoring while meeting operational and compliance requirements.
How can you meet this requirement?
A. Push the container image to OCIR, build a serverless function using the OCI Functions serviceBYOD (Bring-Your-Own-Dockerfile) feature, build an API deployment specification with serverless functions as the back-end, and use an OCI API gateway to provide front- end access to that function.
B. Push the container image to the OCI code repository, create an instance template with a Docker container running the image, and create an instance pool with autoscaling configuration. Use the OCI load balancer to provide an API endpoint to connect with the microservice.
C. Push the container image to the OCI code repository, build a serverless function using the OCI Functions service BYOD feature, build an API deployment specification with serverless functions as the back-end, and use an OCI API gateway to provide front-end access to that function.
D. Push the container image to OCIR, create an instance template with a Docker container running the image, and create an instance pool with autoscaling configuration. Use the OCI load balancer to provide an API endpoint to connect with the microservice. -
Question 9:
Your customer recently ordered for a 1-Gbps Fast Connect connection In ap-tokyo-1 region of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). They will us this to one Virtual cloud Network (VCN) in their production (OC1) tenancy and VCN In their development OC1 tenancy
As a Solution Architect, how should yon configure and architect the connectivity between on premises and VCNs In OCI?
A. Create two private virtual circuits on the FastConnect link. Create two Dynamic Routing Gateways, one for each VCNs. Attach the virtual circuits to the dynamic routing gateways.
B. You cannot achieve connectivity using single FastConnect link as the production and the development VCNs-are in separate tenancies. Request one more FastConnect connection.
C. Create a single private virtual circuit over FastConnect and attach fastConnect to either of the VCN's Dynamic Routing Gateway. Use Remote Peering to peer production and development VCNs.
D. Create a hub-VCN that uses Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG) to communicate with on- premises network over FastConnect. Connect the hub-VCN to the production VCN spoke and with development VCN spoke, each peered via their respective local Peering Gateway (LPG) -
Question 10:
Give this compartment structure:
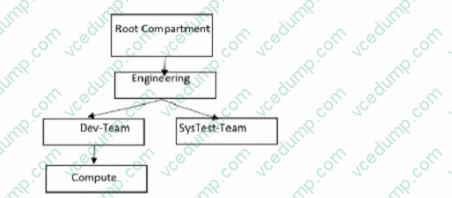
You want to move a compute instance that is in 'Compute' compartment to 'SysTes-Team'. You login to your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)account and use the 'Move Resource' option.
What will happen when you attempt moving the compute resource?
A. The move will be successful though Compute Instance and its Public and Private IP address will stay the same. The Compute instance VNIC will need to be moved separately. The Compute instance will still be associated with the original VCN.
B. The move will fail and you will be prompted to move the VCN first. Once VCN is moved to the target compartment, the Compute instance can be moved.
C. The move will be successful though Compute Instance Public and Private IP address changed, and it will be associated to the VCN in target compartment.
D. The move will be successful though Compute Instance and its Public and Private IP address will stay the same. The Compute instance VNIC will still be associated with the original VCN.
Related Exams:
-
1Z0-020
Oracle8i: New Features for Administrators -
1Z0-023
Architecture and Administration -
1Z0-024
Performance Tuning -
1Z0-025
Backup and Recovery -
1Z0-026
Network Administration -
1Z0-034
Upgrade Oracle9i/10g OCA to Oracle Database OCP -
1Z0-036
Managing Oracle9i on Linux -
1Z0-041
Oracle Database 10g: DBA Assessment -
1Z0-052
Oracle Database 11g: Administration Workshop I -
1Z0-053
Oracle Database 11g: Administration II
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Oracle exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your 1Z0-997-22 exam preparations and Oracle certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.
